- Arthroscopy
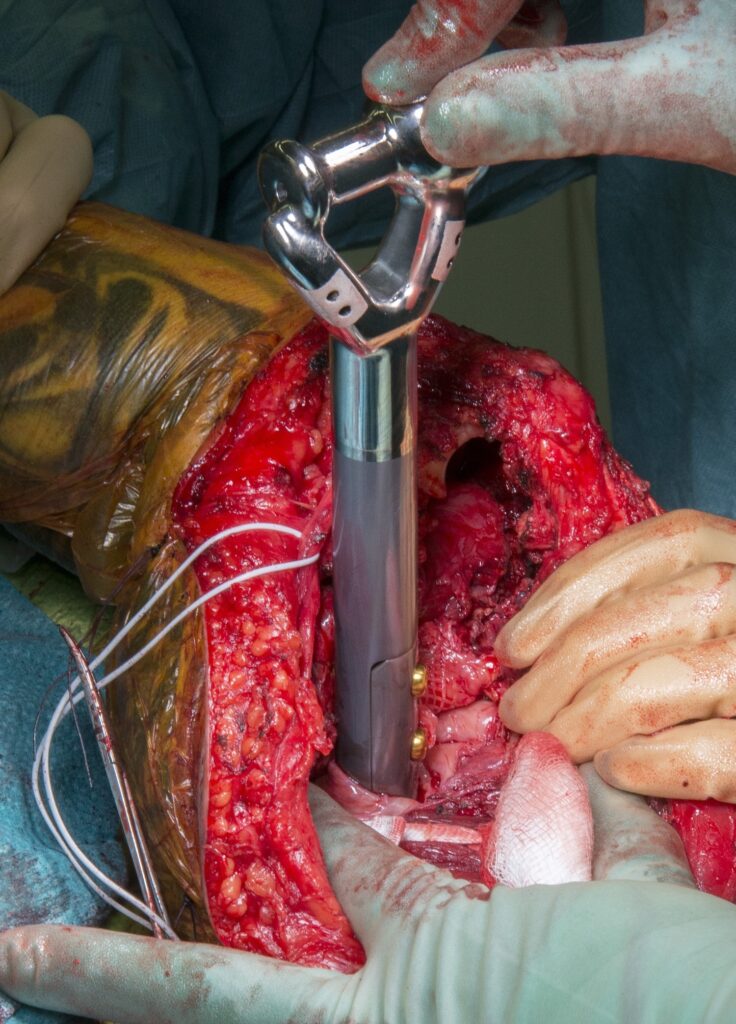
This image is brought to you by OrthOracle, the online e-learning Orthopaedic surgery atlas. Click here to Take the tour.. In association with Wheeless Textbook of Orthopaedics. - Arteries of the Upper Limb
- Aspiration of Elbow
- Biceps - distal tendon rupture
- Capitulum Fractures
- Condylar Fractures/ Pediatric Condylar Frx
- Coranoid Process Frx
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
- Elbow in the R.A. Patient
- Dislocations of the Elbow
- Distal Humeral Physeal Separation
- Flexion Contracture of the Elbow
- Hetertopic Bone Formation
- Lateral Epicondylitis
- Medial Collateral Ligament
- Medial Epicondylitis
- Monteggia Frx
- Nurse Maid's Elbow
- Olecranon - Frx
- Osteochondritis Dissecans
- Osteochondrosis of the Medial Epicondyle
- Panner's Disease
- Pediatric Condylar Fractures
- Pediatric Elbow Injuries
- Pediatric Radiology
- Physical Exam
- Posterolateral Instability
- Puncture of
- Radial Head Excision
- Radial Head Fractures
- Radial Head Replacement
- Radial Head Subluxation
- Radial Neck Fracture
- Rheumatoid Elbow

