- Discussion:
- RA manifests itself in many ways in elbow joint, including nodules and bursae, synovitis, progressive joint destruction, antecubital cysts, & ulnar or, rarely posterior interosseous palsy;
- note that involvement of the RA elbow is infrequently an isolated and therefore it is important to consider possible involvement in the wrist and shoulder;
- Synovitis:
- antecubital cysts usually occur during acute episodes of extremely hyperplastic synovitis due to herniation of synovium thru relatively weak anterior capsule of joint;
- nerve palsies also result from synovial herniation;
- ulnar nerve: (see cubital tunnel)
- in case of ulnar nerve, pressure may arise from protrussion of synovium under transverse section of MCL bridging gap between posterior and anterior bands of that structure;
- synovial cyst confined to cubital tunnel formed by posterior surface of medial epicondyle anteriorly & arcuate ligament posteriorly can readily give rise to ulnar neuropathy;
- posterior interosseous nerve syndrome:
- any protrussion from synovium is likely to displace PIN against sharp tendinous margins of origin of ECRB & superficial humeral lamina of supinator (ligament of Frohse);
- paralysis of posterior interosseous nerve will result in loss of finger extension and should be distinguished from extensor tendon rupture;
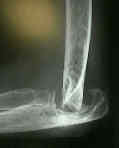
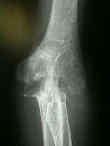
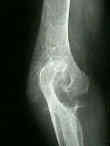
- Stages:
1: soft tissue swelling and osteoporosis
2: mild narrowing of the joint space and some marginal erosion;
- consider steroids injections, synovectomy, & possibly w/ excision of the head of the radius;
3: joint space is significantly narrowed;
- main destruction affects humeral-ulnar joint;
- there may occur an anterior subluxation of the radial head;
- here it may act as a mechanical block to flexion & extension, once there is erosive changes in trochlea;
- consider excision of radial head to restore optimal f(x);
- consider total joint replacement for severe intractable pain loss of extension beyond 60 deg, & instability 2nd to severe bone destruction;
4: integrity of subchondral plates is breached by deep erosions;
- there is extensive destructive of humeroulnar joint causing trachlear notch of olecranon to migrate proximally into deficient trochlea of humerus;
- w/ humeroulnar destruction, the radial head may be acting as a major stabilising force against the front of the capitellum;
- hence, radial head excision may worsen instability;
- at this stage of the disease consider joint replacement;
5: total joint destruction w/ complete loss of normal articular surface
- ironically, as pt passes from stage 4 to stage 5, pt may become pain free, in a way achieveing self arthoplasty;
- Synovectomy:
- pain should be a major indication for this procedure;
- as noted by Gendi NS, et al (1997), strongest predictor of good results was limited pronation/supination w/ retained flexion-extension;
- cummlative survival was 81% at one year and decreased 2.6% per year;
- limited flexion-extension was an independent risk factor for a poor result;
- patients may expect better gains in pronation and supination than flexion/extension;
- gains in supination are especially appreciated by patients, because supination cannot be well compensated for by shoulder motion (unlike pronation which is compensated for by shoulder abduction);
- references:
- Arthroscopic and open synovectomy of the elbow in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Synovectomy of the elbow in rheumatoid arthritis. Long-term results.
- Elbow synovectomy and excision of the radial head in rheumatoid arthritis: a short term palliative procedure.
- Elbow synovectomy in rheumatoid arthritis. Long-term results.
- Synovectomy of the elbow and radial head excision in rheumatoid arthritis. Predictive factors and long-term outcome.
- Arthroscopic synovectomy of the elbow in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Surgery for rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow: a comparison of radial-head excision and synovectomy with total elbow replacement.
- Total Elbow Replacement
Surgical treatment of the elbow in rheumatoid arthritis.