 - Trauma Workup
- Trauma Workup
- assessment of perfusion: damage control orthopaedics
- timing of surgery in orthopaedic patients with brain injury
- surgical timing and prevention of pulmonary complications in patients with femur frx
- PreOp Planning for IM Nailing: (IM Nailing Technique)
- Fracture Classification
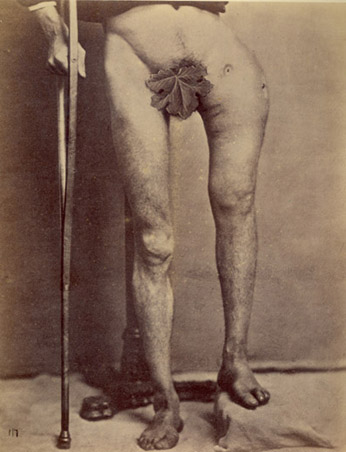
- Open Femur Frx
- Comminuted Frx
- Proximal Frx
- Distal Frx
- Associated Injuries/Conditions:
- Frx - Menu
- Hip Dislocation
- Femoral Neck Frx
- need to proactively determine whether a femoral neck fracture is present;
- some recommend reconstruction nails for all femur fractures, inorder to prophylactically fix the potentially missed fracture;
- references:
- Accuracy of reduction of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures--an analysis of various internal fixation strategies.
- Diagnosis of femoral neck fractures in patients with a femoral shaft fracture. Improvement with a standard protocol.
- Fracture of the ipsilateral neck of the femur in shaft nailing. The role of CT in diagnosis.
- A retrospective review of high-energy femoral neck-shaft fractures.
- Iatrogenic fractures of the femoral neck during closed nailing of the femoral shaft.
- A cascade of preventable complications following a missed femoral neck fracture after antegrade femoral nailing.
- Is reconstruction nailing of all femoral shaft fractures cost effective? A decision analysis.
- The sensitivity of ct scans in diagnosing occult femoral neck fractures.
- Bilateral Femur Frx:
- references:
- Mortality after reamed intramedullary nailing of bilateral femur fractures.
- Invited commentary related to: "Are Bilateral Femur Fractures No Longer a Marker for Death?
- Morbidity and Mortality of Bilateral Femur Fractures
- Knee Ligament Injury
- Ipsilateral diaphyseal femur fractures and knee ligament injuries.
- Injuries to the knee ligaments with fractures of the femur.
- Ipsilateral knee injury with femoral fracture. Examination under anesthesia and arthroscopic evaluation.
- Delayed detection of clinically significant posterior cruciate ligament injury after peri-articular fracture around the knee of 448 patients.
- Pathologic Fracture
- C-spine
- Spine
- Pelvis / Abdomen:
- Delayed Internal Fixation of Femoral Shaft Fracture Reduces Mortality Among Patients with Multisystem Trauma
- Femoral Shaft Fractures Associated With Unstable Pelvic Fractures.
- Pulmonary: (assessment of perfusion: damage control orthopaedics)
- fat embolism syndrome:
- prevention of pulmonary complications in patients with femur frx
- Vascular Injury
- references
- Blunt Vascular Injury Associated With Closed Mid-Shaft Femur Fracture: A Plea for Concern.
Timing of Surgery in Orthopaedic Patients with Brain Injury
- Systems:
- Neuro (see Glasgow)
- Cranio-Maxillo-Facial
- Spine
- Cardiac
- Renal
- Compartments
- Hepatic / GI
- Coag
- Checklist:
- Consent: Open vs Closed Reduction
- Posting
- Blood & Cell Saver
- Implant Selection (Synthes)
- Positioning
- Table type and Flouro (specify locations of each in the room)
- Skeletal Traction
- skeletal traction w/ 25 lbs (or more) will bring frx out to length;
- generally skeletal traction is necessary w/ delayed treatment;
- following insertion of skeletal traction, it is necesary to document that frx is out to length w/ portable lateral radiograph;
- ref: Preoperative Skeletal Versus Cutaneous Traction for Femoral Shaft Fractures Treated Within 24 Hours.
- Blood: 2 units
- Prophylactic ATB
- DVT prophylaxis
- X-rays and Template
- Planned Incision
- Anesthesia & Cardiology Consults
- Misc: antibiotic beads for open frx;
- Initial Orders:
- NPO p Midnight x Meds
- IVF D5W LR at 100 ml/hr (in stable patients use D5W 1/2 NS w/ 20 KCl)
- 2 large bore IV
- Foley
- Monitoring;
- EKG and/or Continuous Cardiac Monitoring;
- Continuous Pulse Ox monitoring;
- PreOp Labs:
- Type & Cross 2-4 units pRBC and/or FFP
- Musculoskeletal Labs:
- Urinalysis
- Meds (Trade Names)
- Prophylactic ATB
- DVT prophylaxis
- Steroids:
- for neurological deficits
- for FES prophylaxis
- Heparin 5000 units SQ q8 hrs
- Insulin (1/2 NPH dose) + S.S. - Accu Check in AM and on call
- Zantac
- Morphine
- Tetanus or Pneumovax if appropriate;
- Traction: (Buck's vs. Skeletal)
- Decubiti Prophylaxis: Egg Crate / Pillow and turn 20 deg q2hr
- Hiboclens Shower and Bactroban to nares q12 hrs until OR
- Cleocin solution 300 mg per 100 ml NS q6hr as mouth wash
- Misc:
- Mechanism: high energy injuries from MVA or GSW, or Pathologic frx;
- fails in tensile strain;
- common mech is bending Transverse frx;
- pathologic frx are more commonly spiral after torsion strain

