- See:
- Caput Ulnae Syndrome
- Rheumatoid Hand
- Wrist Arthrodesis
- Discussion:
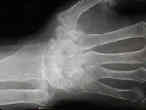
- wrist involvement w/ RA is common;
- findings inlude peri-articular osteoporosis, destructive osteolysis, arthritis of distal RU joint, and carpal arthrosis;
- final pattern is one of volar & ulnar carpal subluxation, radial deviation of the hand, and intercarpal supination;
- flexor tendon rupture:
- extensor tendon rupture:
- rupture or attenuation of radial wrist extensors;
- concomitant dorsal tenosynovitis is differentiated from inflammed carpal synovium by noting whether the inflammatory tissue moves as the fingers are flexed and extended;
- may be due to dislocation of RU joint;
- radial side:
- attenuation of radioscapholunate & radiocapitate ligament;
- joint erosion & progressive capsular stretching results in ulnar displacement of proximal carpal bones w/ secondary radial deviation of hand;
- radiocarpal joint:
- scaphoid & lunate slip into palmar position on radius;
- rotation (supination) of carpus on radius
- radial metacarpal shift
- volar dislocation of carpus beneath radius;
- bony erosion of volar carpus
- in some cases radius & lunate become spontaneously fused;
- rotatory displacement of scapoid and SLD;
- DISI deformity may occur because of disruption of scapholunate ligament;
- ulnar side:
- attenuation of ulno-carpal ligaments
- volar displacement of ECU (becomes flexor rather than extensor)
- volarflexion intercalary segment instability (VISI) pattern may be present because of destruction of ulno-carpal ligament;
- ulnar translocation:
- radio-ulnar joint: (see anatomy)
- ulnar translocation of carpus
- caput ulnae syndrome (dorsal prominence of ulna);
- dislocation of RU joint;
- results from destructive synovitis involving TFCC;
- pain and limitation of motion;
- may cause extensor tendon rupture;
- MP joints
- PreOp Considerations:
- begin w/ proximal joints first: shoulder > elbow > wrist > hand;
- begin with predicatabler procedures;
- carpal tunnel release
- tenosynovectomy
- wrist stabilization
- distal ulnar resection;
- then begin with less predictable and more complicated surgery;
- thumb surgery
- DIP fusion
- MP arthroplasty
- PIP arthroplasty etc.
- Treatment Methods:
- teno-synovectomy:
- ECRL to ECU transfer:
- indicated for correctable radial deviation deformity (or wrist supination deformities), especially if there is a loss of active wrist ulnar deviation; (deformity must be passively correctable);
- frequently MP-ulnar deviation will be present, which may require additional surgery;
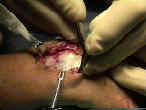
- technique:
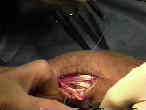
- standard longitudinal approach to the wrist;
- enter dorsal retinaculum thru the ECU tendon sheath;
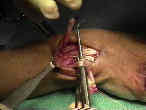
- elevate the retinaculum radially to the second extensor compartment;
- isolated the ECRL to the musculotendinous junction, and distal end is freed;
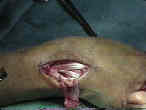
- the extensor retinaculum is split and the distal half is passed deep to the tendons and the proximal half is place superficial to the extensor tendons;
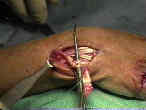
- ECRL is woven into the ECU (superficial to the extensor tendons and retinaculum);
- tension is adjusted until the wrist maintains a neutral position;
- tendon is passed superficial to the other wrist extensors and is anchored to the ECU with the wrist in a neutral position;
- references:
Tendon transfer for radial rotation of the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis.
Radiologic evaluation of the rheumatoid hand after synovectomy and extensor carpi radialis longus transfer to extensor carpi ulnaris.
- dislocation of RU joint:
- often due to destructive synovitis of TFFC;
- may lead to extensor tendon rupture and painful limited motion;
- treatment options:
- Darrah's procedure with reconstruction of the TFFC and the joint capsule;
- Sauve Kapandji
- Hemi-resection Arthroplasty of RU Joint
- radiocarpal arthrodesis:
- indicated for early radiocarpal volar subluxation (if there is no mid-carpal deformity);
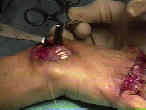
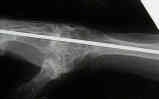
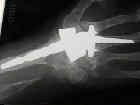
- wrist arthrodesis:
- indicated for significant deformity of radiocarpal joint;
- consider concomitant RU joint arthroplasty;
- w/ severe deformity, consider wider exposure to the first dorsal compartment in order to allow excision of the radial styloid;
- carpometacarpal joints are usually not included in the fusion;
- wrist position:
- unlike conventional wrist fusion (performed for traumatic DJD), the rheumatoid wrist should be fused in slight flexion;
- remember that the rheumatoid patient will often have difficult with MP extension (not flexion), and therefore, the wrist should be fused in slight flexion to promote extensor tenodesis effect;
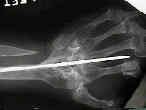
- internal fixation:
- dorsal plate may cause wound slough;
- consider fixation w/ Steinman pin directed between the index and long web space, through the carpi, and then into the distal radius;
- a second pin can be directed from the third web space into the radius;
- Considerations for Wrist Prosthesis:
- balance of extensor tendons is of primary importance, esp ECRB;
- if this tendon is ruptured, there is no effective wrist extension;
- one should not confuse ECRL or EDC when evaluating for f(x) of ECRB;
- if active wrist extension does not go beyond neutral, or if there is significant palmar carpal subluxation, integrity of ECRB should be questioned;
- when ECRB tendon is not intact, wrist arthrodesis is indicated
Long-term results of Swanson silastic arthroplasty in the rheumatoid wrist.
Swanson silicone arthroplasty of the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis: a long-term follow-up.
Limited arthrodesis for the rheumatoid wrist.
Palmar shelf arthroplasty. A follow-up note.
Palmar shelf arthroplasty in the rheumatoid wrist. Results of long-term follow-up
Extensor digiti minimi tendon transfer to prevent recurrent ulnar drift.
Comparison of arthroplasty and arthrodesis for the rheumatoid wrist.