- Indications:
- painful or unstable wrist joint w/ advanced destruction due to OA, RA, post traumatic arthritis, SLAC wrist, spastic flexion
contracture, degenerative scaphoid non-union, unsuccessful wrist arthroplasty, and Keinbock's dz;
- this procedure is more beneficial for young, active pts or middle aged pts, but not for elderly pts;
- PreOp Considerations:
- in the rheumatoid wrist note that application of a dorsal plate increases the chances of dorsal wound dehiscence;
- ulnocarpal impaction
- if preoperative radiographs demonstrate abutment between between the distal ulna and the triquetrum in addition to loss of
supination, then consider the need for radial lengtening w/ bone graft;
- bone grafting:
- cancellous bone grafting (iliac or local) is sufficient when there is no significant loss of carpal bone stock nor cyst formation;
- cortico-cancellous bone grafting may be indicated w/ severe bone resorption or significant cyst formation
(however, complication rate is higher);
- ROM of other joints:
- remember that the elbow and shoulder joints will have to compensate for loss of wrist motion;
- Dorsal Approach to the Wrist:
- w/ severe deformity, consider wider exposure to the first dorsal compartment inorder to allow excision of the radial styloid;
- individual carpal bones and distal radius are exposed w/ wrist hyperflexion;
- articular cartilage is removed w/ rongeur;
- proximal row carpectomy:
- consider performing a proximal row carpectomy procedure so that the proximal capitate and hamate are fused into the distal
radial surface;
- the proximal row carpectomy is especially indicated for patients with ulnar positive varience, because it eliminates
common occurence of ulnotriquetral impingement following arthrodesis;
- after proximal carpal row is excised, the carpi can be used as bone graft;
- the standard fusion technique then procedes on, using the standard fusion plate;
- references:
- Capitate-radius arthrodesis: an alternative method of radiocarpal arthrodesis.
- Wrist arthrodesis in post traumatic arthritis: a comparison of two methods.
- fusion:
- most surgeons prefer not to fuse the index CMC joint;
- whether to fuse the long CMC joint remains controversial (sparing the joint allows it to participate in power grip);
- ref: AO-wrist arthrodesis: with and without arthrodesis of the third carpometacarpal joint.
- intrinsic compartment release:
- it has been observed that intrinsic tightness in the of the index and long digits is a frequent complication of wrist fusion,
and may be related to occult compartment syndrome;
- to manage this potential problem, consider releasing the dorsal fascial compartments;
- ulnar head:
- in RA consider resection of the ulnar head, and then using it for bone graft;
- Position of Arthrodesis:
- w/ non RA wrist, 10 deg of dorsiflexion is ideal because its allows position for power gripping;
- maximum grip is generated in 35 deg of dorsiflexion but this interferes with ADL's;
- in pts w/ RA (see RA wrist), neutral or flexed position is more desirable;
- position of 5-10 deg of ulnar deviation is perferred in order to counter balance zig zag collapse and ulnar drift;
- note that despite the usual recommendations, some patients will prefer slightly more flexion or extension in the wrist;
- if possible, consider casting the wrist before surgery in extension and the neurtral position to determine which position is
more comfortable for the patient;
- reference:
- The relationship between wrist position, grasp size, and grip strength.
- Methods of Fixation:
- pin Fixation:
- in the report by Rehak DC, et al (2000), the authors compared use of pin fixation vs 3.5 mm reconstruction plate;
- wrists showed a tendency for migration into volar flexion (3-6 deg) from the initial intra-operative position;
- 3.5 mm reconstruction plate:
- in the report by Rehak DC, et al (2000), the authors compared use of pin fixation vs 3.5 mm reconstruction plate;
- technique involved placement of the extensor retinaculum beneath the extensor tendons;
- 3-4 screws are placed in the distal radius and two screws are placed in metacarpal, and if possible one screw in capitate;
- wrists had an average 5 deg of extension and 5 deg of ulnar deviation;
- A comparison of plate and pin fixation for arthrodesis of the rheumatoid wrist.
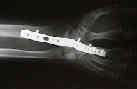
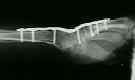
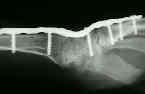
- synthes plate:
- 8 hole titanium, w/ 2.7 mm screws inserted into the distal 4 holes, and 3.5 mm holes in the proximal 4 holes;
- in order to have the wrist in 10 deg of dorsiflexion, a contoured plate is necessary;
- often the dorsal articular lip will have to be sculpted and Lister's tubercle will have to be removed in order to achieve a flat
bed for the plate;
- most often the plate is applied to the long metacarpal so that 3 cortical screws can be inserted into the metacarpal and 4
screws in the radius (often a screw will also be inserted into the capitate)
- in some cases, the plate will be attached to the index metacarpal, if this optimizes the wrist position (for ulnar deviation)
or if it optimizes plate fit;
- in some cases, the plate must be placed obliquely across the dorsal radial surface inorder to get the optimal amount of
ulnar deviation;


- Wound Closure:
- consider detaching the ECRB insertion and then moblizing it over the plate and incorporating it into the capsular closure (this may
help prevent wound dehicience;
- Post Op:
- Volar splint for 2 weeks;
- unionn is usually achieved by 3 months;
- plate is not removed unless it causes symptoms;
- Complications:
- extensor tenosynovitis most common complication and is related to prominent plate and screws;
- intrinsic contracture;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- non union of the CMC joint;
- RU joint instability:
- ulno-carpal abutment:
- reference:
- Ulnocarpal abutment after wrist arthrodesis.
Wrist arthrodesis in paralyzed arms of children.
Wrist arthrodesis in rheumatoid arthritis. A comparison of two methods of fusion.
Arthrodesis of the Wrist for Post Traumatic Disorders.
Complications following AO/ASIF wrist arthrodesis.
Long-Term Follow-Up Study of Radiocarpal Arthrodesis for the Rheumatoid Wrist.