 - Discussion:
- Discussion:
- anatomy and ligamentous contraints:
- ligaments of the wrist
- SL interosseous ligament
- SLD is most common and most significant ligament injury of wrist; (carpal instability);
- risk factors: ulna minus configuation, slope of radial articular surface, and lunotriquetral coalition;
- spectrum of injury: (increasing severity)
- ref: Association of lesions of the scapholunate interval with arthroscopic grading of scapholunate instability via the geissler classification.
- dynamic scapholunate instability
- no radiographic evidence of malalignment is present (ie dynamic deformity);
- diagnosis is established by dorsal S-L tenderness and positive shift test;
- ref: The Role of the Flexor Carpi Radialis Muscle in Scapholunate Instability
- rotatory subluxation of scaphoid:
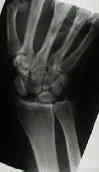
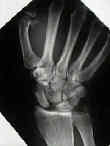
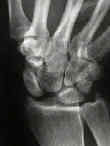
- scapholunate dissociation (SLD):
- SL ligament tear may lead to rotational dislocation of scaphoid allowing proximal pole to displace posteriorly & distal pole
to displace anteriorly;
- scaphoid inherently tends to palmar flex because of its oblique position and the loading applied thru (STT) joint;
- because scaphoid lacks proximal of ligament, it will rotate around radiocaptitate ligament leading to dorsal rotary
subluxation of the proximal pole;
- dorsal intercalated segment instability: (DISI)
- scapholunate advanced collapse:
- mechanism of injury:
- mechanism is similar is similar to that of scaphoid frx w/ stress loading of extended carpus, except it is usually in ulnar rather
than radial deviation;
- w/ a severe hyperextension injury of the wrist, there is tear of scapholunate interosseous ligament;
- further loading causes tear of (in succession);
- radiocapitate ligaments;
- radiotriquetral ligaments;
- dorsal radiocarpal ligaments;
- lunate follows triquetrium into extension, & DISI deformity results;
- associated injuries:
- simultaneous radial styloid frx is relatively common w/ carpal dislocation;
- always consider non-displaced scaphoid frx;
- diff dx:
- scaphoid impaction syndrome (SIS);
- occult ganglion cyst;
- posterior interosseous nerve neuroma;
- ulnar translocation:
- physiologic scapholunate separation such as lunotriquetral coalition (compare to other hand);
- perilunate dislocation (which has be reduced and splinted)
- references:
- Is this scapholunate joint and its ligament abnormal?
- Wide scapholunate joint space in lunotriquetral coalition: a normal variant?
- Coincident rupture of the scapholunate and lunotriquetral ligaments without perilunate dislocation: pathomechanics and management.
- Radiographic Findings: in Scapholunate Dislocation:
- Traction radiography for the diagnosis of scapholunate ligament tears.
- Exam for Scapholunate Instability
- Non Operative Treatment:
- non operative treatment can only be recommended for dynamic scapholunate instability;
- suggested measures include: activity modification, NSAIDS, and wrist splinting;
- references:
- Chronic asymptomatic contralateral wrist scapholunate dissociation.
- Obvious radiographic scapholunate dissociation: X-ray the other wrist.
- Treatment Options for Acute Tears:
- manipulation & closed pinning:
- may correct a fresh scapholunate dissociation;
- flex & ulnar deviate the wrist to produce lunate reduction & flexion;
- consider retrograde insertion of K wire thru scaphoid and out radial side of wrist, pulling K wire out radially, and then
advancing K wire into ulna;
- be aware that K wire insertion may displace lunate;
- K wire should be inserted into distal cortex of lunate, but midcarpal joint should be left free to absorb small movements;
- scaphoid should be pinned similarly if not perfectly reduced to lunate;
- reduction of scaphoid is achieved w/ thumb pressure dorsally over proximal pole;
- avoid distraction using slow insertion under flouroscopy;
- screw fixation:
- Reduction and Maintenance of Scapholunate Dissociation Using the TwinFix Screw
- The use of temporary screw augmentation for the treatment of scapholunate injuries.
- Chronic scapholunate instability treated with temporary screw fixation.
- Scapholunate Temporary Screw Fixation for the Treatment of Chronic Scapholunate Instability
- HERBERT SCREW FIXATION FOR THE TREATMENT OF SCAPHOLUNATE LIGAMENT RUPTURE
- Treatment of Scaholunate Instability with Internal Screw fixation
- acute ligament repiar:
- dynamic reconstruction:
- Dynamic Repair of Scapholunate Dissociation With Dorsal Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Tenodesis
- Brunelli Tenodesis :
- Distal Tunnel Placement Improves Scaphoid Flexion With the Brunelli Tenodesis Procedure for Scapholunate Dissociation
- Treatment Options for Chronic Tears: Capsulodesis:
- dorsal intercarpal ligament capsulodesis:
- this technique does not tether the scaphoid to the distal radius (as does the blatt capsulodesis), the technique may
permit good closure of the scapholunate gap without restricting wrist motion;
- in the study by Slater, et al (1999), the dorsal intercarpal ligament capsulodesis reduced SLD gap formation down to 1 mm vs
3.7 mm using the blatt dorsal capsulodesis technique;
- technique:
- 5 mm wide flap of dorsal IC ligament (triquetral-trapezoidal) is elevated off trapezoid (left attached to triquetrum);
- scaphoid is taken out of its flexed position (finger on the scaphoid tubercle) and the scapholunate gap is reduced;
- flap is then rotated down, stretched as tightly as possible, and is then attached to the distal pole of the scaphoid (about
3-4 mm proximal to the STT joint);
- Dorsal intercarpal ligament capsulodesis for scapholunate dissociation: biomechanical analysis in a cadaver model.
- blatt dorsal capsulodesis:
- involves creation of a flap of wrist capsule (left attached to the radius) which is inserted onto the dorsal pole of the scaphoid;
- the fact that there remains a tether to the distal radius may infact be a disadvantage of this procedure;
- can be used instead of, or in addition to, the repair of the ligament, and can be performed for chronic dynamic instability as
well as for chronic SLD;
- capsulodesis keeps scaphoid from subluxating in palmar direction and corrects flexed posture of scaphoid;
- disadvantages: fails to correct the diastasis and significantly decreases wrist ROM;
- technique:
- dorsal capsular flap is left attached to radius proximally & is then subsequently inserted in distal part of the scaphoid to
tether distal pole dorsally;
- length of the dorsal capsular flap from the origin at the distal radius to the STT joint;
- references:
- Capsulodesis in reconstructive hand surgery. Dorsal capsulodesis for the unstable scaphoid and volar capsulodesis following excision of the distal ulna.
- Dynamic scapholunate instability: results of operative treatment with dorsal capsulodesis.
- Treatment of scapholunate dissociation by ligamentous repair and capsulodesis.
- Dorsal intercarpal ligament capsulodesis for chronic, static scapholunate dissociation: Clinical results
- Radiographic evaluation of the modified Brunelli technique versus the Blatt capsulodesis for scapholunate dissociation in a cadaver model.
- Four-bone ligament reconstruction for treatment of chronic complete scapholunate separation.
- Long-term results of dorsal intercarpal ligament capsulodesis for the treatment of chronic scapholunate instability
- STT fusion
- scapholunate fusion:
- mentioned only to be condemned;
- expect non union rates over 90%;
- references:
- Scaphocapitolunate arthrodesis.
- Scaphoid-trapezium-trapezoid fusion in the treatment of chronic scapholunate instability.
- Treatment of scapholunate dissociation. Rotatory subluxation of the scaphoid.
- A comparison of scaphoid-trapezium-trapezoid fusion and four-bone tendon weave for scapholunate dissociation.
- Attempted scapholunate arthrodesis for chronic scapholunate dissociation.
- Treatment of scapholunate dissociation: preferred treatment--STT fusion vs other methods.
- Long-term follow-up of scaphoid-trapezium-trapezoid arthrodesis.
- Evaluation of the biomechanical efficacy of limited intercarpal fusions for the treatment of scapho-lunate dissociation.
- Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC):
- Proximal Row Carpectomy
- 4 Corner Fusion
- Wrist Fusion
- references
- Fascial implant arthroplasty for treatment of radioscaphoid degenerative disease.
- On resection of the proximal carpal row.
- Proximal row fusion as a solution for radiocarpal arthritis.
- Scaphoid excision and capitolunate arthrodesis for radioscaphoid arthritis.
- Treatment of scapholunate dissociation by ligamentous repair and capsulodesis.
- Radio-scapho-lunate partial wrist arthrodesis following comminuted fractures of the distal radius.
Symposium--Progress in Sports Medicine: Athletic Injuries of the *Wrist.*
Scapholunate Stabilization With Dynamic Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Tendon Transfer
Proximal row carpectomy for scapholunate dissociation