(see: Synthes Femoral Products)
- Anatomy of Femur
- Arterial supply
- Canal Entry Point
- Comminuted Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Distal Femoral Physeal Fractures
- Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Discussion of Femur
- DVT and PE arising from Trauma and L.E. Fractures
- External Fixation for Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Femoral Neck Frx associated w/ Femoral Shaft Frx
- Femoral and Tibial Traction Pins
- Floating Knee Injuries
- Infected IM nails
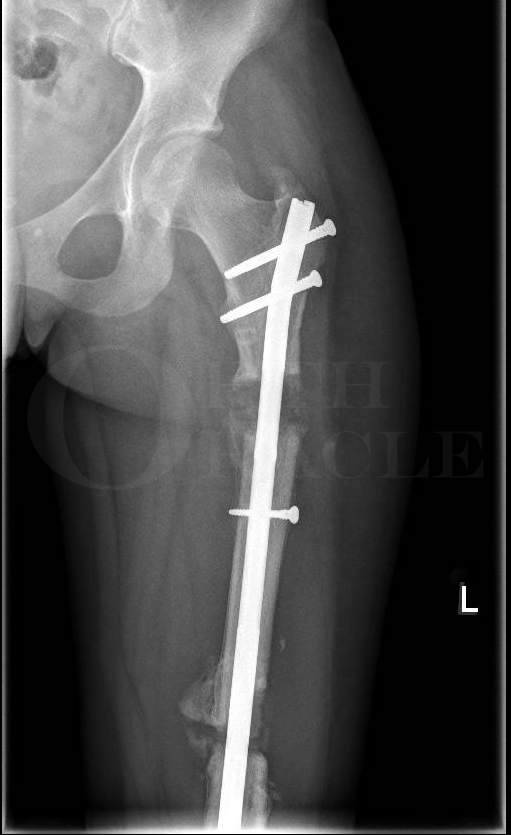
- Intramedullary Nailing
- Open Fractures
- Nonunion
Pediatric Femoral Fractures »
- Plating of Femoral Shaft Frx
- Periprosthetic Fracture
- Prophylactic IM Nailing (metastatic disease)
Proximal Femoral Shaft Fractures - Reaming and Nailing Maneuver
- Reduction of Femoral Shaft Frx
- Retrograde Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Subtrochanteric Fractures
- Supracondylar Fractures
- Synthes IM Femoral Nail
- Timing of Surgery in Orthopaedic Patients with Brain Injury
- Winquist Class
- Universal Femoral Distractor