- See: 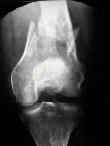
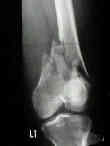
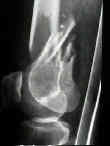
- Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Distal Femoral Phyeal Frx
- Supracondylar Fractures following TKR
- Discussion:
- work up for femur fracture
- mechanism: axial load to a flexed knee;
- Bimodal distribution:
- low energy fractures involving older females (often have
severe osteoporosis);
- high energy fractures involving younger males;
- associated injuries:
- vascular Injury: 2-3% (similar to vessel injury in knee dislocations)
- knee ligament injuries: 20% (most commonly the ACL)
- tibial plateau fractures are also common;
- pertinent surgical anatomy
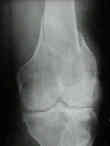
- Radiographs: (see: AO classification (Muller))
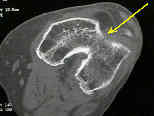
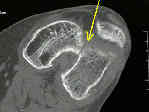
- must r/o a Hoffa extension (coronal plane fracture) in which case, a condylar buttress plate is required;
- tunnel view of the intercondylar notch is helpful in judging the displacement of vertical fractures into the jonit;
- in elderly patients who sustain low energy fractures it may be difficult to determine whether there is an intra-articular component;
- in these cases, consider obtaining a CT scan;
- Operative Treatment: (discussion and surgical approach)
- open supracondylar frx
- 95 deg. condylar blade plate
- dynamic screw and side plate
- condylar buttress plate
- locking plate fixation: (see general concepts)
- locking condylar plates (synthese menu)
- pearls:
- pre-contoured plates are general under contoured compared to native femoral anatomy;
- often first screw is inserted proximally into the cortex so that proper proximal-distal plate position is obtained;
- if screw is tightened down all the way, under-contoured plate will cause fracture reduction distortion (medialization of frx);
- consider loosely applying this screw so that it maintains the plate position, but allows the distal locking screws to
properly engage the distal fragment;
- once the distal screws have been inserted, the original proximal screw can be fully tightened down, which should result
in an optimally reduced fracture;
- rotational alignment:
- considerations for healing:
- non union may be as high as 20%;
- Non-union in lateral locked plating for distal femoral fractures: A systematic review.
- bone healing with plates
- fracture union is more likely when there are empty holes in the plate adjacent to fractures;
- references:
- Additional fixation of medial plate over unstable lateral locked plating of distal femur fractures: A biomechanical study.
- Failure of LCP Condylar Plate Fixation in the Distal Part of the Femur. A Report of Six Cases.
- 2010 mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: healing complications are common after locked plating for distal femur fractures.
- Dynamization of locked plating on distal femur fracture
- Open distal femur fractures treated with lateral locked implants: union, secondary bone grafting, and predictive parameters.
- Dynamic fixation of distal femur fractures using far cortical locking screws: a prospective observational study.
- Motion Predicts Clinical Callus Formation: Construct-Specific Finite Element Analysis of Supracondylar Femoral Fractures.
- Relationships between Hoffa fragment size and surgical approach selection: a cadaveric study
- IM nails for supracondylar fractures:
- Internal fixation of supracondylar femoral fractures: comparative biomechanical performance of the 95-degree blade plate and two retrograde nails.
- these authors used a modified retrograde IM nail (blade inserts into nail), and noted better stability than seen with
standard blade plate except in torsion
Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur. Treatment by internal fixation.
Double-plating of comminuted, unstable fractures of the distal part of the femur.
Supracondylar fracture of the femur following prosthetic knee arthroplasty.
Surgical treatment of displaced, comminuted fractures of the distal end of the femur.
Rush-pin fixation of supracondylar and intercondylar fractures of the femur.
Physeal arrest about the knee associated with non-physeal fractures in the lower extremity.
Supracondylar fracture of the femur: closed or open reduction?
Supracondylar femoral fractures in the frail elderly. Fractures in need of treatment.
The Treatment of Open Distal Femur Fractures With Immediate Open Reduction and Internal Fixation. Helpenstell T, et al. J Orthop Trauma. 1991;5:235.
Supracondylar fractures of the femur treated by external fixation.
Treatment of Supracondylar Nonunions of the Femur with Plate Fixation and Bone Graft.