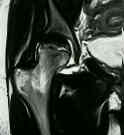
Discussion:
- pathogenesis - vascular interruption:
- blood supply to femoral head
- specific inciting causes
- natural history
- diff dx:
- synovitis;
- Idiopathic Transient Osteoporosis of the Hip
- femoral neck stress frx
- metastatic disease
- trochanteric bursitis:
- ref: Avascular necrosis of the femoral head presenting as trochanteric bursitis.
- prognosis:
- in general, patients with confirmed AVN have a 70-80% chance of collapse after 3 years;
- in the series of 72 hips (general population) w/ MRI changes c/w AVN (followed by Ito H, et al (1999)), 64% became symptomatic;
- necrotic lesions greater than 2/3 of the wt bearing portion of the femoral head on T1 central coronal images;
- of these hips 75% became symptomatic, where as 25% remain asymptomatic after 6 years;
- in the study by Bizot P, et al (1998), 35 patients w/ bilateral AVN following bone marrow transplant were followed;
- of these 70 hips, 56 hips went on to collapse;
References
- Prediction of Collapse with Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head.
- Prognosis of early stage avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
- Natural history of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
- Femoral head osteonecrosis after bone marrow transplantation.
- Osteonecrosis of the femoral head after solid organ transplantation: a prospective study.
- Asymptomatic Osteonecrosis: Should It Be Treated?
- Radiographic Studies: 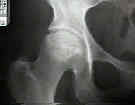
- x-rays:
- ficat classification
- In Brief: Ficat Classification: Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head
- enneking's stages of osteonecrosis
- bone-scanning:
- magnetic resonance imaging:
- preferred method for dx of occult AVN, since its more sensitive than bone scan or plain films;
- note high incidence of bilateral AVN, and that MRI may pick up AVN in opposite asymptomatic hip;
Treatment: Stages I, II, and III
- medications:
- anticoagulation agents:
- Enoxaparin Prevents Progression of Stages I and II Osteonecrosis of the Hip.
- bisphosphonates:
- fosamax: this medication may interfere with resorption of necrotic bone, which may delay subchondral collapse and progression of arthrosis;
- references:
- The use of alendronate to prevent early collapse of the femoral head in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis. A randomized clinical study.
- Does Zoledronate Prevent Femoral Head Collapse from Osteonecrosis?
- electromagnetic fields:
- core decompression:
- free vascularized fibular grafting:
References

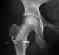 - Fate of Very Small Asymptomatic Stage-I Osteonecrotic Lesions of the Hip.
- Fate of Very Small Asymptomatic Stage-I Osteonecrotic Lesions of the Hip.
- Spontaneous Resolution of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head.
- Capacitive coupling as an adjunctive treatment for avascular necrosis.
- Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on Steinberg ratings of femoral head osteonecrosis.
- Treatment: Stages III, IV and V:
- resurfacing arthroplasty:
- indicated for later stages of disease in addition to disease which involves a large portion of the femoral head;
- has had only intermittent success in the past, but w/ modern components there has been renewed interest;
- it is possible that resurfacing arthroplasty will emerge as the procedure of choice for AVN;
- note that a mismatch between the size of the prosthesis and the acetabulum may contribute to unfavorable restults;
- it is probably important that sizes be available in at least 2 mm increments;
- in the study by Hungerford, et al (1998), 33 femoral resurfacing procedures in 25 patients who had stage-III or IV osteonecrosis of femoral head;
- 30 hip prostheses (91 percent) survived for a minimum of five years;
- at a mean of 10.5 years (4-14 years) postop, 16 (62 %) of the 26 hips with stage-III disease had a good or excellent Harris hip score;
- majority underwent this procedure using a modified anterolateral approach, to preserve the remaining posterior blood supply to the femoral head;
References
- Precision fit surface hemiarthroplasty for femoral head osteonecrosis: long-term results.
- Surface Replacement Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head.
- Is bipolar hemiarthroplasty a reliable option for Ficat stage III osteonecrosis of the femoral head? 15- to 24-year follow-up study
- total hip arthroplasty:
- ongoing concern over cement disease, particulate matter, and stress shielding changes in the femur in cemented or non-cemented
prostheses makes a total hip arthroplasty a less desirable option;
- bipolar arthroplasty:
- references:
- Bipolar versus total hip arthroplasty for avascular necrosis of the femoral head. A comparison.
- Clinical and motion studies of the Bateman bipolar prosthesis in osteonecrosis of the hip.
- Bipolar prosthetic replacement for the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
- Bipolar versus total hip arthroplasty for hip osteonecrosis in the same patient.
- Acetabular diameter measurement determines proper prosthetic head size in hemiarthroplasty for femoral head osteonecrosis.
- Is bipolar hemiarthroplasty a reliable option for Ficat stage III osteonecrosis of the femoral head? 15- to 24-year follow-up study.
- arthrodesis:
- arthrodesis of the hip has been used in some series, but because of 50-80 % prevalence of bilaterality of AVN, this may be poor choice
References
Current Concepts: Nontraumatic Necrosis of Bone (Osteonecrosis).
Recent Advances in Great Britain--Symposium: Caisson Disease of Bone.
Bicentenary Festschrift: Segmental Vascular Changes in the Femoral Head in Children and Adults.
Multimodality approach to osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A prospective randomized treatment protocol.
Precision-fit surface hemiarthroplasty for femoral head osteonecrosis. Long-term results