 - See:
- See: - Anastomosis of lower limb arteries
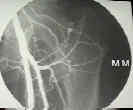
- Arterial supply of the femur
- AVN of femoral head;
- AVN following femoral neck fracture
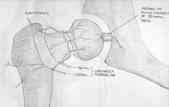
- Anatomy:
- extracapsular arterieal ring at the base of the femoral neck;
- formed posteriorly by large branch of MFCA
- formed anteriorly by smaller branches of LFCA;
- superior & inferior gluteal artery have minor contributions;
- ascending cervical branches
- these give rise to retinacular arteries;
- gives rise to subsynovial intra articular ring
- artery of ligamentum teres;
- derived from obturator or MFCA;
- inadequate to supply femoral head with displaced fractures;
- forms the medial epiphyseal vessels;
- only small & variable amount of the femoral head is nourished by artery of ligamentum teres;
- ref: The ligamentum teres of the adult hip
- epiphyseal blood supply:
- arises primarily from lateral epiphyseal vessels that enter head posterosuperiorly;
- vessels from medial epiphyseal artery entering thru ligamentum teres;
- epiphyseal arterial branches:
- arise as arteries of subsynovial intraarticular ring;
- two groups of epiphyseal arteries: lateral & inferior vessels;
- metaphyseal blood supply:
- arises from extracapsular arterial ring;
- arise from branches of ascending cervical arteries, & subsynovial intra articular ring;
- Changes w/ Age:
- even after closure of epiphyseal plate, there is minimal astomosis between epiphyseal and metaphyseal circulations;
- in the adult, greatest portion of blood supply to head of femur is derived from vessels on posterior superior surface of femoral neck;
- Femoral Neck Frx:
- frx disrupts intraosseous cervical vessels;
- portion of the neck that is intracapsular has essentially no cambium layer in its fibrous covering to participate in peripheral
callus formation;
- hence, healing is dependent on endosteal union alone;
- femoral head nutrition is then dependent on remaining retinacular vessels, & supply from the ligamentum teres;
- position acheived at reduction is significant factor in development of avascular necrosis:
- in frx of hip, valgus reduction may end up kinking of lateral epiphyseal vessels & tethering of medial epiphyseal
vessels in ligamentum teres;
- valgus and rotatory malposition may result in AVN
The relative contribution of the medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries to the vascularity of the head and neck of the femur: a quantitative MRI-based assessment.
Intracapsular pressure and caput circulation in nondisplaced femoral neck fractures.
The arterial supply of the developing proximal end of the human femur.
Vascularity of the hip labrum: a cadaveric investigation.
Capsular and Pericapsular Contributions to Acetabular and Femoral Head Perfusion
Vascular Supply to the Acetabular Labrum

