- Discussion:
- stress frx of femoral neck are relatively uncommon injuries, with most reports involving military recruits & athletes who are subjected to increased physical demands;
- like most stress frx, women are most often affected and it is important to inquire about amenorrhea and occult eating disorders;
- these patients will also require an osteoporosis work up and quantification of bone density;
- patients may note groin pain that is made worse with activity and that is relieved with rest;
- diff dx: AVN and transient osteoporosis;
- Radiographs:
- initial radiographs are often normal, but even late radiographs may fail to show reactive changes;
- radiographic evidence of disruption of both cortices or frx widening is indication for prompt internal fixation to prevent displacement;
- classification of stress frx:
- stress frxs are classified as either tension or compression frx;
- compression frxs occur on the inferior aspect of the femoral neck;
- look for internal callus at the inferior femoral neck;
- tension fractures occur on the superior aspect of the femoral neck;
- causes a transverse fracture across the femoral neck;
- this fracture type is more likely to progress and displace;
- Bone Scan / MRI:
- bone scan or MRI is necessary to identify the fracture; 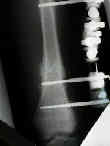
- MRI:
- is an alternative to bone scan and allows an early diagnosis;
- look for decreased signal intensity on T1 and increased signal on T2;
- see NEJM teaching case;
- Nonsurgical Treatment
- must include frequent serial radiographs to detect any changes in frx pattern or displacement.
- compression frxs occur on the inferior aspect of the femoral neck;
- are more stable than tension frxs & generally can be treated w/o surgery if no frx line is present;
- non operative therapy consists of a period of bed rest followed by protected wt bearing;
- serial radiographs are manditory;
- Surgical Treatment:
- fractures of both cortices must undergo immediate internal fixation;
- tension fractures occur on the superior aspect of the femoral neck;
- they are potentially unstable & should undergo internal fixation;
- see technique of cannulated screw insertion;
- Complications:
- AVN may follow a delay in diagnosis
Stress fractures of the femoral neck in athletes. The consequence of a delay in diagnosis.
Insufficiency stress fractures of the femoral neck in elderly women.
Femoral neck stress fractures in children and adolescents.
Atypical Tensile-Sided Femoral Neck Stress Fractures. The Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Subchondral Fatigue Fracture of the Femoral Head in Military Recruits.
Displaced Femoral Neck Fatigue Fractures in Military Recruits.
Long-term outcome of undisplaced fatigue fractures of the femoral neck in young male adults.

