- Amputation of the Finger and Hand
- Arthrodesis of the MP joint and Finger Joints
- Boutonnere Injuries
- Characteristics of Phalangeal and Metacarpal Fractures
- Compression Screws
- Condylar Frx
- Crossed Finger Flap
- Dislocations of PIP
- Digit Reimplantation
- Dislocations:
- Dorsal Dislocation of the PIP joint
- Dorsal Dislocation of the DIP joint
- Dorsal Dislocation of the Thumb IP joint
- Rotary PIP Subluxation
- Volar PIP Dislocation
- Extensor Tendon Mechanism
- Extension Block Casting
- Extra-Octave Frx
- F.D.P. Avulsion
- Finger Incisions
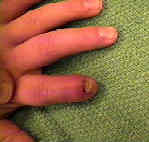
- Finger Tip Injuries
- Fractures:
- Distal Phalangeal Frx
- Fracture Dislocations of the PIP Joint
- Middle Phalanx Frx
- Pediatric Phalangeal Frx
- Proximal Phalanx Fracture
- Thumb Fractures
- Grayson's Ligament
- Lateral Bands
- Mallet Deformity / Fractures
- Nail Bed Injuries
- Oblique Retincular Ligament
- Paronychia
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: PIP Joint
- Skin and Soft Tissue Replacement in the Hand
- Surgical Approaches
- Swan Neck Deformity
- Tendon Injuries
- Thumb Deformities in RA
- Thumb Soft Tissue Defects
- Transverse Retinacular Ligament
- Trigger Finger
- Anatomy:
- length of 3 phalangeal segments follows closely ratio of 1:1.618 (golden mean) of Fibonacci series discovered by Leonardo de Pisa
- thus from distal to proximal, the length of each phalanx is sum of length of the more distal two segments;
- this normal skeletal relationship & alignment will keep intrinsics & extrinsic muscle tendon units in equilibrium;
- PIP Joint:
- PIP joint is essentially a hinge joint, allowing only flexion and extension, and is more stable than MP joint;
- vast majority of PIP collateral ligament ruptures occur at proximal attachment;
- on stress x-ray, angulation of < 20 deg implies good prognosis;
- checkrein ligaments;
- swallotail extensions of volar plate along volar proximal phalanx which may thicken producing PIP flexion contracture;
- during release of checkrein ligaments, protect transverse communicating vessels, which supply vincular system, & lie underneath checkreins, and merge in the midline;
- Exam:
- finger aligment & rotation:
- determined by noting relationship of fingernails w/ digits in full extension and in flexion;
- area of precise PIP joint tenderness:
- dorsal (central slip), radial/ulnar (collateral lig.), volar (volar plate)
- inability to actively extend the PIP joint against resistance is diagnostic of rupture of central slip (boutonnere lesion);
- Fracture Dislocations of the PIP Joint
- Complications of Treatment:
- malrotation:
- avoided only by noting rotational symmetry of fingernails;
- also note symmetry of flexed fingers which should normally point to the tubercle of scaphoid;
- spiral fractures produce rotary deformities;
- malunion: seen after spiral, transverse, or articular frx;
- muscle imbalance: seen w/ transverse frxs;
- stiffness following frx:
- may be related to improper positioning of the hand after reduction;
- articular fractures may become are often associated with delays in union due to fibrinolysis in the synovial fluid;
- best results are obtained when joint becomes stiff in neutral position;
- treatment:
- when joint is stiff in extension, transverse retinacular ligaments are transected;
- then collateral ligaments are transected from dorsal to palmar until passive motion is regained;
- flexion contracture:
- Resurfacing Arthroplasty:
- indicated for traumatic arthritis of PIP joint;
- volar plate can be used & advanced across painful, stiff PIP joint;
- may achieve up to 80% of normal & good pain reduction


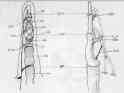
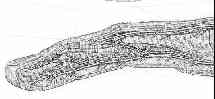
Use of the anterior branch of the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve as a graft for the repair of defects of the digital nerve.
The conservative management of volar avulsion fractures of the P.I.P. joint.
Year Book: Chip Avulsions and Ruptures of the Palmar Plate in the PIP
The Hueston flap in reconstruction of fingertip skin loss: results in a series of 41 patients.
Nail bed repair and reconstruction by reverse dermal grafts.
An innervated cross-finger flap for fingertip reconstruction.
The use of lateral V-Y advancement flaps for fingertip reconstruction.
Extensor tenolysis: a modern version of an old approach.
Early results with osseointegrated proximal interphalanageal joint prosthesis.

