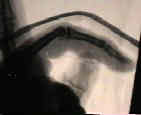
- See: Phalangeal Injury
- Discussion:
- takes advantage of stabilizing forces of flexor & intrinsic on phalanges with the MP joint held in 90 deg flexion;
- intact dorsal extensor mechanism functions as "tension band" to palmar cortex, and helps maintain the reduction;
- digital rotation and angulation are largerly controlled by having four digits move together;
- Indications:
- Proximal Phalanx Frx;
- closed dorsally angulated transverse frx;
- short oblique shaft frx;
- impacted base proximal phalangeal fractures;
- PIP dorsal dislocations
- Technique:
- anesthesia: metacarpal or wrist block;
- fracture is reduced w/ longitudinal traction w/ MP in maximal flexion;
- buddy tapping the digits maintains rotational control and improves stability;
- splint:
- wrist in 30 deg of extension;
- MP joints in 90 deg of flexion,
- on dorsal side cast is extended to PIP joint;
- leave PIP joint free;
- phalanges should have full range of flexion;
- begin active digital motion
Extension Block Pinning for Unstable Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Dorsal Fracture Dislocations