- Discussion: 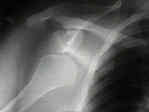

- ON THE ARTICULATIONS. by Hippocrates.
- pathoanatomy:
- bankart lesion
- hill sachs lesion
- stabilizers of the shoulder:
- dynamic / muscular stabilizers
- static stabilizers
- anteroinferior glenohumeral ligament
- references:
- Pathoanatomy of first-time, traumatic, anterior glenohumeral subluxation events.
- mechanism of anterior dislocations:
- combination of abduction, extension, and a posteriorly directed force applied to the arm;
- humeral head is driven anteriorly, tearing shoulder capsule, detaching labrum from glenoid, and producing a compression
fracture of humeral head;
- arm position during the traumatic episode leads to variations of anterior dislocation
- associated injuries
- references:
- Mechanisms of glenohumeral joint stability.
- Lesions in different types of anterior glenohumeral joint dislocation. An experimental study.
- classification of anterior dislocation:
- chronic unreduced dislocations
- fracture dislocation
- multidirectional instability
- recurrent anterior instability
- natural history
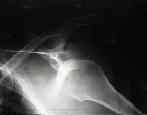
 - Physical Exam:
- Physical Exam:
- associated injuries
- Radiographic Studies:
- Apical Oblique View
- Axillary View
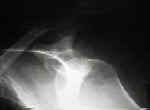
- Hill Sachs Lesion
- True AP - (35 deg oblique to the body)
- Transscapular View
- Stryker Notch view for picking up a Hill Sachs;
- West Point Axillary View:
- osseous bankart defect on anteroinferior glenoid rim;
- discussion:
- common radiographic changes seen following anterior dislocations, include Hill Sachs lesion, calcification along the antero-
inferior aspect of the glenoid rim (or fracture of the glenoid rim);
- additional findings include fracture, erosion, blunting of the anterior glenoid rim;
- osseous bankhard deformities:
- references:
- What Is the Critical Value of Glenoid Bone Loss at Which Soft Tissue Bankart Repair Does Not Restore Glenohumeral
Translation, Restricts Range of Motion, and Leads to Abnormal Humeral Head Position?
- The critical size of a defect in the glenoid causing anterior instability of the shoulder after a Bankart repair, under
physiological joint loading
![]()
- Initial Treatment of Dislocation:
- work up for shoulder dislocation
- reduction methods
- Non Operative Treatment:
- natural history:
- may be indicated for patients w/ multidirectional instability, for voluntary instability, for posterior
glenohumeral instability, & for those who need a supranormal ROM - such as baseball pitchers;
- references:
- Immobilization after primary dislocation of the shoulder.
- Treatment of instability of the shoulder with an exercise program.
- Conservative treatment of fractures and fracture-dislocations of the upper end of the humerus.
- Treatment of primary anterior shoulder dislocation in patients older than 40 years of age. Conservative verus operative
- Immobilization in external rotation after shoulder dislocation reduces the risk of recurrence. A randomized controlled trial.
- Redislocation of Shoulder During First 6 Weeks After a Primary Anterior Dislocation: Risk Factors and Results of Treatment
- [Conservative therapy of antero-inferior glenoid fractures].
- Position and duration of immobilization after primary anterior shoulder dislocation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature.
- Return to Play and Recurrent Instability After In-Season Anterior Shoulder Instability. A Prospective Multicenter Study
- Surgical Treatment:
- Open Anterior Shoulder Reconstruction: (anterior approach to shoulder)
- Arthroscopic Shoulder Reconstruction
Diagnosis and treatment of traumatic anterior instability of the shoulder.
Hypoplasia of the glenoid. A review of sixteen patients.
Anterior shoulder instability.
Acute shoulder dislocations: factors influencing diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of chronic glenoid defects in the setting of recurrent anterior shoulder instability: a systematic review
Anterior Capsulolabral Reconstruction of the Shoulder in Athletes in Overhand Sports.
The diagnosis and treatment of anterior instability in the throwing athlete.
Dislocation arthropathy of the shoulder.

