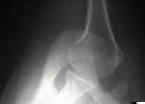
- Discussion:
- best true lateral view of shoulder;
- Allows Evaluation of:
- head compression frx: (allows assessment of presence and size);
- lesser tuberosity
- lesser tuberosity is seen anteriorly as a small inverted V on anterior surface of the humeral head;
- glenoid frxs
- posterior dislocation
- anterior instability (see anterior dislocation)
- normally there is posterior translation of humeral head when arm is placed in extension and external rotation;
- posterior translation is result of tension in anterior capsule & ligaments;
- this posterior translation is absent in shoulders w/ anterior instability;
- Os Acromiale:
- Os acromiale: anatomy and surgical implications.
- Technique:
- must be taken w/ arm abducted, not necessarily to 90 deg (optimal)
- cassette is placed on the superior aspect of the shoulder;
- arm is abducted enough to allow the radiographic beam to pass between chest and the arm in a direction perpendicular to cassette from shoulder;
- Trauma Axillary View:
- does not require abduction of the arm (nor removal from sling);
- the patient leans backward;
- the x-ray plate is placed directly under the shoulder, and the x-ray tube is positioned directly above
Roentgenographic evaluation of suspected shoulder dislocation: a prospective study comparing the axillary view and the scapular 'Y' view.