 - See: Radiology of the Acetabulum
- See: Radiology of the Acetabulum
- Discussion:
- instability = cephalic displacement of posterior sacroiliac complex of at least 5-15 mm on inlet and outlet views;
- look for gap (rather than impaction) posteriorly, & frx of 5th lumbar transverse process or avulsion of sacrospinous ligament;
- Pertinent Radiographs:
- AP view
- Inlet and Outlet Views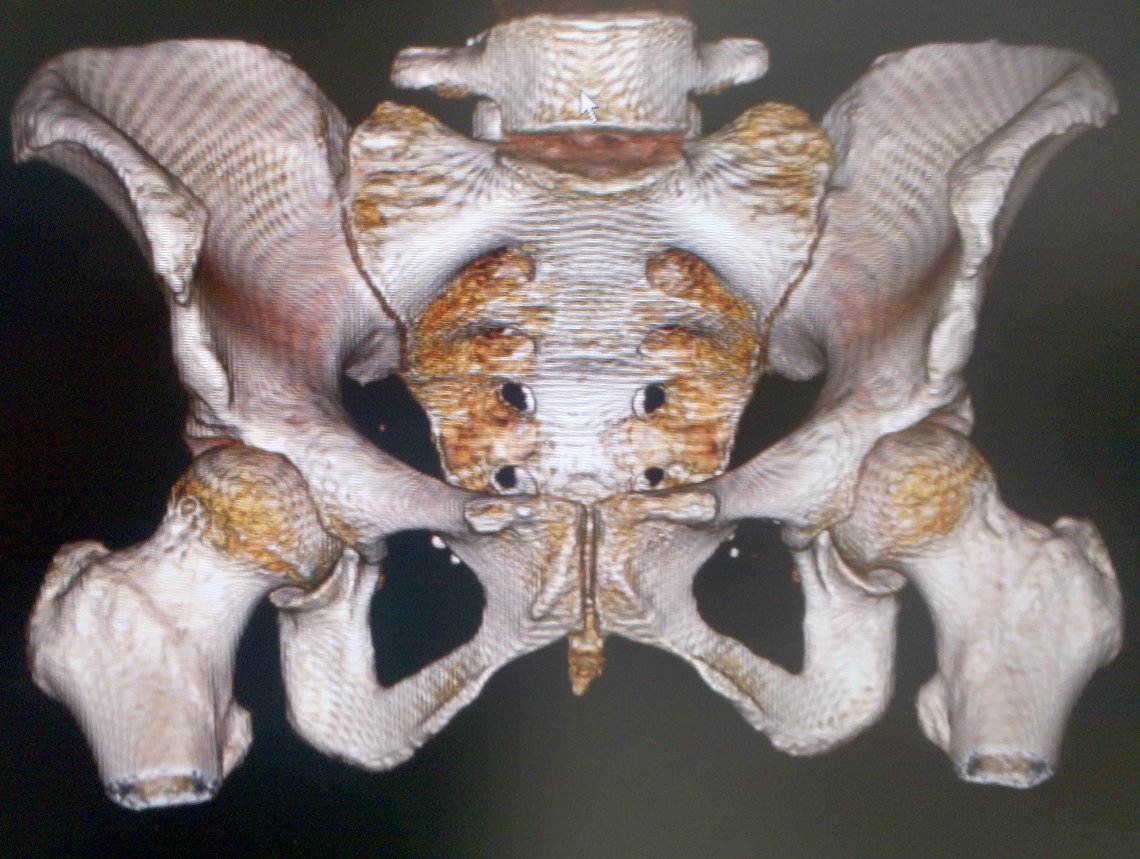
- Judet View
- Push-Pull Views:
- used to evaluate dynamic displacement of the pelvis;
- these views are obtained as in outlet view with the examiner pushing on the femur for one view and pulling on it for the other;
- Sacroiliac Views:
- used to visualize the sacroiliac joints;
- pt is positioned as for Judet views w/ central beam directed toward sacroiliac joint;
- only CT scan of the pelvis gives well detailed image of SI joint;
- neither the iliac or obturator oblique radiographs shows this well;
- Lateral View:
- required if sacral frx is suspected;
- technique is identical to lateral view of lumbar spine except that it is centered on the sacrum;
- Arteriography:
- indicated for patients w/ concomitant pelvic frx and hemodynamic instability, especially when there is frx displacement thru the greater sciatic notch
Is a fracture of the transverse process of L5 a predictor of pelvic fracture instability?
Pelvic and Lower Extremity Trauma--Symposium: The Role of Standard Roentgenograms in the Evaluation of Instability of Pelvic Ring Disruption.
The role of standard roentgenograms in the evaluation of instability of pelvic ring disruption.

