- Discussion: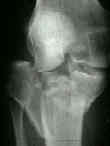
- 60% of plataue frxs involve lateral plateau.
- this probably is result of valgus alignment of lower extremity and fact that most injuring forces are
directed laterally to medially;
- frxs of medial plateau make up 15% & bicondylar lesions 25% of plateau frx;
- bicondylar frxs combine any of unicondylar lesions w/ frx of metaphysis;
- expected frx patterns:
- lateral split fragment - found in 75%;
- posteromedial fragment - seen in 43%;
- tibial tubercle fragment - seen in 16%;
- zone of comminution that including the tibial spine - frequently extends to the lateral
condyle - seen in 28%
- references:
- Tibial Plateau Fracture Characteristics: Computed Tomography Mapping of Lateral, Medial, and Bicondylar Fractures
- partial or complete ligamentous ruptures occur in about 15% to 45% & meniscal lesions in about 5-37% of all tibial plateau frx;
- AO Classification:
- Type I Fracture / Minimally Displaced Fractures
- Type II Fracture: / Split Compression Fractures
- Type III Fracture: / Local Compression Fracture
- Type IV Fractures: / Medial Tibial Plateua Fractures
- Type V Fractures: / Bicondylar Fractures
- Type VI Fractures: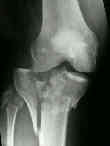
- ref: Classifications in Brief: Schatzker Classification of Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Misc Tibial Plateau
- Fracture Dislocations
- Frx of the Fibula and Tibial Plateua fractures
- Ligamentous Injuries in Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Rim Fractures
- Split Fractures
- Total Depression Fracture
- reference:
- Classification of fractures of the tibial condyles.
- Exam:
- skin abrasion and contussions from direct blows;
- compartment syndrome: occurs in 11%
- ref: Radiographic Predictors of Compartment Syndrome in Tibial Plateau Fractures
- ligamentous instability
- peroneal nerve function;
- Radiographic Studies
- How much articular displacement can be detected using fluoroscopy for tibial plateau fractures?
- Non Operative Treatment
- references:
Closed reduction of tibial plateau fractures. A comparison of functional and roentgenographic end results.
The cast brace and tibial plateau fractures.
Cast brace treatment of proximal tibia fractures. A ten-year follow-up study.
Fractures of the tibial plateau. Treatment by closed reduction and spica cast.
Tibial plateau fractures. A comparison of conservative and surgical treatment.
- Operative Management:
- Work Up and PreOp Planning:
- references:
- Acute compartment syndrome in tibial plateau fractures--beware!
- Influence of prior fasciotomy on infection after open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures.
- Does Early versus Delayed Spanning External Fixation Impact Complication Rates for High-energy Tibial Plateau and Plafond Fractures?
- Surgical Approaches:
- Lateral Plateau
- Medial Plateau
- Percutaneous Fixation:
- references:
- Percutaneous Screw Fixation of Tibial Plateau Fractures.
- Closed reduction and percutaneous screw fixation for tibial plateau fractures
- Indirect reduction and percutaneous screw fixation of displaced tibial plateau fractures.
- How much articular displacement can be detected using fluoroscopy for tibial plateau fractures?
- Elective removal of implants after open reduction and internal fixation of Tibial Plateau fractures improves clinical outcomes.
- IM Nailing:
- A comparative study for complex tibial plateau fractures: nailing and compression bolts versus modern and traditional plating.
- The management of complex fractures of the proximal tibia with minimal intra-articular impaction in fragility patients using intramedullary nailing and compression bolts.
- Adjunctive Procedures:
- Bone Grafting:
- references:
- Interporous hydroxyapatite as a bone graft substitute in tibial plateau fractures.
- Factors influencing the results of open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures.
- Comparison of autogenous bone graft and endothermic Ca phos cement for defect augmentation in tibial plateau frx.
- Outcomes of Schatzker II tibial plateau fracture open reduction internal fixation using structural bone allograft.
- Impaction bone grafting has potential as an adjunct to the surgical stabilisation of osteoporotic tibial plateau fractures:
- Role of Arthroscopy: (see arthroscopy of the knee)
- advantages:
- reduced postoperative pain and swelling;
- early recovery of knee motion, and less postoperative knee stiffness;
- reduced risk of infection
- minimal fragment devascularization
- direct visualization of the articular surface: meniscal lesions (20% of the patients) and osteochondral detachments(25%
of the patients)
- disadvantages:
- lack of rigid fixation and the need for delayed weight-bearing.
- references:
- Arthroscopy of meniscal injuries with tibial plateau fractures.
- The Role of Arthroscopy in the Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures.
- Arthroscopic Restoration of Depressed Tibial Plateau Fractures Using Bone and Hydroxyapatite Grafts.
- Arthroscopic Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures.
- Arthroscopically assisted treatment of lateral tibial plateau fractures in skiers: use of a cannulated reduction system.
- Arthroscopic Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures.
- Arthroscopic Management of Tibial Plateau Fractures.
- The Role of Arthroscopy in the Assessment and Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures.
- Combined arthroscopic treatment of tibial plateau and intercondylar eminence avulsion fractures.
- [Comparison study on effectiveness between arthroscopy assisted percutaneous internal fixation and open reduction and internal fixation for Schatzker types II and III tibial plateau fractures].
- Operatively Treated Meniscal Tears Associated with Tibial Plateau Fractures: A Report on 661 Patients.
- Post Operative Care and Complications
- references:
- Effect of tibial plateau fracture on lubrication function and composition of synovial fluid
Tibial plateau fractures. Management and expected results.
Indications for surgical treatment of tibial condyle fractures.
Limited Internal Fixation of Tibial Plateau Fractures. Rangitsch MR , et al. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7:168.