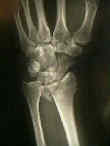
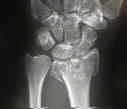
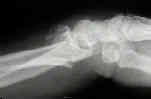
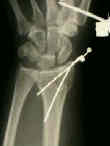
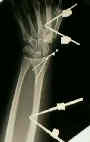
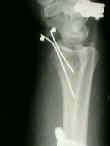
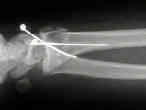
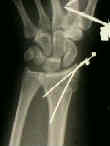
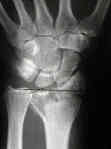
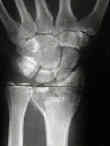
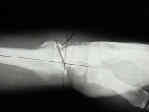
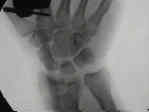
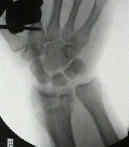
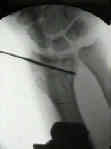
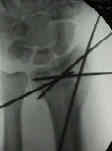
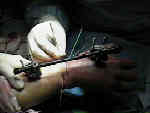
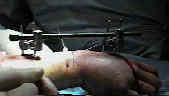
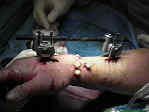
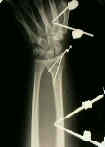
 - See: orthofix fixator
- See: orthofix fixator
- Discussion:
- convential "bridging" external fixation relies on ligamentotaxis to apply traction & restore displacement;
- indications:
- active pts when radial length is decr by > 3-4 mm;
- presence of dorsal comminution;
- when closed reduction fails to restore anatomic palmar tilt;
- for any unstable or intra-articular distal radial frx which can not be held in a reduced posisiton w/ a cast;
- as noted in the study by Trumble, et al (1998), external fixation provided clear advantages in specific situations;
- in older patients, pain relief, grip strength, and ROM were significantly better when external fixation was used;
- in younger patients, external fixation provided consistently better results when there was comminution in 2 or more cortices;
- controversies:
- bridging vs non bridging external fixation:
- conventional external fixtion involves placing the distal pins into the first metacarpal (pins span the wrist joint), whereas non bridging fixators do not span the joint but rather are placed into the distal fracture fragment;
- in the study by McQueen MM, et al (1998), bridging and non-bridging fixators were compared in a randomized prospective study;
- non bridging fixation is not used when there is less than 1 cm of volar cortex or w/ articular displacement;
- more normal volar tilt, carpal alignment, grip strength, and flexion were maintained better in the nonbridging group;
- at one year from injury, the bridging fixator group showed a mean dorsal tilt of 12.2 deg vs 5.6 deg in the non bridging group;
- the authors point out that the non bridging fixator does not distract the wrist joint, and therefore allows better ROM both during fixator placement and following fixator removal;
- references
- Redisplaced unstable fractures of the distal radius. A randomised, prospective study of bridging versus non-bridging external fixation.
- Intraarticular fractures of the distal radius: a cadaveric study to determine if ligamentotaxis restores radiopalmar tilt.
- Intrafocal (Kapandji) pinning of distal radius fractures with and without external fixation.
- Radiographic Findings: (Melone Classification)
- Surgical Technique:
- positioning:
- ensure that the flouroscopic monitor is placed at the patient's head;
- this will allow the surgeon to look straight ahead as pins are inserted from the radial styloid to the ulnar cortex of the radius;
- perform an initial closed reduction under flouroscopy; 
- surgical technique for fixator application:
- metacarpal pin insertion;
- radial pin insertion;
- initial reduction w/ fixator:
- ligamentotaxis:
- distraction facilitates articular reduction and restoration of palmar tilt;
- w/ inadequate reduction following application of Ex Fix, consider insertion of percutaneous pins or limited ORIF;
- it may necessary to apply wrist flexion and ulnar deviation inorder to maintain a temporary reduction;
- percutaneous K wires
- reduction and final wrist position:
- avoid over distraction of wrist joint:
- ulnar styloid fracture:
- if frx involves ulnar styloid, place upper extremity in a long arm posterior splint in mid supination for 3-4 weeks;
- bone grafing: (bone graft menu)
- w/ depression more than 5 mm, make a small longitudinal extra-articular incision over the dorsal fracture site to provide bone graft;
- Leung, et al reported on 100 distal radius fractures radius in which iliac bone graft was used to support the reduction;
- they removed the external fixators frame at 3 wks and used a functional brace for an additional 3 wks.
- they noted few complications, & there was maintenance of reduction w/ good or excellent function in nearly all patients;
- references:
- An effective treatment of comminuted fractures of the distal radius.
- Cancellous grafting and external fixation for unstable Colles' fractures.
- Post Operative Care:
- references:
- Severe fractures of the distal radius: effect of amount and duration of external fixator distraction on outcome.
- Case Examples:
External fixation for intra-articular fractures of the distal radius.
Cast or external fixation for fracture of the distal radius. A prospective study of 126 cases.
Plaster cast versus external fixation for unstable intraarticular Colles' fractures.
Limited open surgical approach for external fixation of distal radius fractures.
Dynamic external fixation for comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius.
Treatment of forearm fractures by Hoffman external fixation. A study of 93 patients.
Hand and wrist function after external fixation of unstable distal radial fractures.
Pattern of forearm fractures in children.
Year Book: Unstable Colles' Fractures in Elderly Patients: A Randomised Trial of External Fixation for Redisplacement.
Dynamic external fixation for comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius.
Cancellous grafting and external fixation for unstable Colles' fractures.