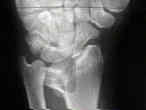
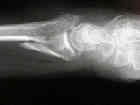
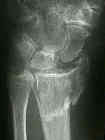
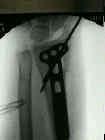
- Discussion: (distal radius fracture menu and colles fracture) 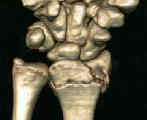
- volar surface of distal part of radius is slightly flattened, except for its distal margin, which
slopes volarly to form a prominent ridge from which volar radiocarpal ligaments originate.
- short radiolunate ligament originates off of volar margin of lunate facet and attaches to
volar surface of lunate and helps maintaining stability of the radiolunate articulation;
- ulnar volar margin of lunate facet slopes volarly as viewed from proximal to distal and may not be
effectively supported by standard implants;
- volar rim of the distal part of the radius is not straight but slopes volarly from radial to ulnar;
- ulnar aspect of the volar rim of the radius is convex distally, forming a palmar prominenceof the lunate facet;
- volar lunate facet extends more distally than is expected, which makes it more difficult to achieve adequate support w/
volar plate fixation;
- fractures of lunate fossa:
- volar shearing fracture with comminution creates a functional radiolunate ligament avulsion, which can lead to instability;
- volar aspect of the lunate fossa bears more load than the scaphoid fossa;
- fractures involving the volar lunate facet articular fragment can therefore be difficult to treat;
- references:
- Loss of Fixation of the Volar Lunate Facet Fragment in Fractures of the Distal Part of the Radius
- The volar extension of the lunate facet of the distal radius: a quantitative anatomic study.
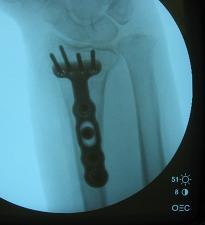 - controversies: should associated ulnar styloid frx be fixed at the time of ORIF?
- controversies: should associated ulnar styloid frx be fixed at the time of ORIF?
- ref: Should an ulnar styloid fracture be fixed following volar plate fixation of a distal radial fracture?
- Preoperative Planning:
- exam:
- if there is significant swelling the case may have to be delayed;
- patients should be examined for carpal tunnel symptoms before and after reduction;
- carpal tunnel symptoms that do not resolve following reduction will require carpal tunnel release;
- radiographs distal radius frx:
- w/ volar Barton's frx, note whether there is more ulnar or radial sided comminution (since this can affect
choice of surgical approach);
- intra-articular frxs w/ > 2 millimeters of displacement;
- restoration of articular anatomy is most critical factor in obtaining a good functional result;
- wrist traction, 2 K wires, one parallel to joint line;
- risk factors for inadequate reduction (unstable fracture)
- dorsal comminution;
- interposition of volar soft tissues;
- tendency for dorsal displacement & dorsal angulation;
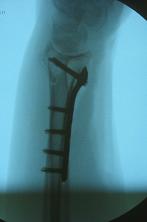 - ref: No Difference in Adverse Events Between Surgically Treated Reduced and Unreduced Distal Radius Fractures.
- ref: No Difference in Adverse Events Between Surgically Treated Reduced and Unreduced Distal Radius Fractures.
- Surgical Approach and Plate Position:
- dorsal approach and fixation:
- ref: - Combined Dorsal and Volar Plate Fixation of Complex Fractures of the Distal Part of the Radius.
- anterior approach and fixation:
- reduction:
- have assistant apply traction as three point reduction is applied directly with surgeon fingers and thumb;
- single k wire through the radial styloid for extraarticular fractures and an addition k wire parallel to the
joint line for intra-articular frxs
- internal fixation: (implants for distal radius fractures):
- plating techniques: (Synthes Distal Radius Plates)
- plate placement:
- distal end of plate should be placed far enough proximally to avoid insertion of screws into articular surface;
- be aware of the watershead line;
- references:
- Volar Locking Plate Implant Prominence and Flexor Tendon Rupture
- Effect of distal radius volar plate position on contact pressure between the flexor pollicis longus tendon and the distal plate edge.
- Volar Plate Position and Flexor Tendon Rupture Following Distal Radius Fracture Fixation
- Three-dimensional kinematics of the flexor pollicis longus tendon in relation to the position of the FPL plate and distal radius width.
- contour plate:
- bend plate to comform to the normal configuration of the radius (contour plate around the radial styloid);
- apply locking adaptors on each end of the plate and use these to radially controur plate;
- screw placement
- consider insertion of ulnar screws first to ensure that there is no joint tresspass (radial screws obstruct view
of ulnar screws);
- screws placed in diaphyseal bone will act as a butress for distal fragment;
- screw length
- references:
- The effects of screw length on stability of simulated osteoporotic distal radius fractures fixed with volar locking plates
- Predicting a safe screw length for volar plate fixation of distal radius fractures: lunate depth as a marker for distal radius depth.
- The dorsal tangential X-ray view to determine dorsal screw penetration during volar plating of distal radius fractures.
- Radiographic evaluation of dorsal screw penetration after volar fixed-angle plating of the distal radius: a cadaveric study.
- Comparison of 4 fluoroscopic views for dorsal cortex screw penetration after volar plating of the distal radius
- Dorsal Screw Penetration With the Use of Volar Plating of Distal Radius Fractures: How Can You Best Detect?
- restoration of volar tilt
- ref: Leveraging the Plate: Reliably Restoring Volar Tilt of Distal Radius Fractures
- final radiographic evaluation:
- references:
- Fluoroscopic evaluation of intra-articular screw placement during locked volar plating of the distal radius: a cadaveric study.
- Use of articular wrist views to assess intra-articular screw penetration in surgical fixation of distal radius fractures.
- Comparison of 4 Fluoroscopic Views for Dorsal Cortex Screw Penetration After Volar Plating of Distal Radius
- Risk Assessment of Tendon Attrition Following Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures With Volar Locking Plates Using Audible Crepitus and Placement of the Plate: A Prospective Clinical Cohort Study.
- Post Operative Care:
- Accelerated rehabilitation compared with a standard protocol after distal radial fractures treated with volar open reduction and internal fixation: a prospective, randomized, controlled study..
- references:
- Loss of Fixation of the Volar Lunate Facet Fragment in Fractures of the Distal Part of the Radius.
- Complications following internal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking-plate.
- References
- A comparative study of clinical and radiologic outcomes of unstable colles type distal radius fractures in patients older than 70 years: nonoperative treatment versus volar locking plating.
- Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures: ORIF with a volar fixed-angle tine plate versus external fixation.
- Volar fixation of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures using the 2.4-mm locking compression plates.
- Functional outcome and complications after volar plating for dorsally displaced, unstable fractures of the distal radius.
- Operative management of distal radial fractures with 2.4-millimeter locking plates. A multicenter prospective case series.
- Prospective study of distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate system
- A randomized prospective study on the treatment of intra-articular distal radius fractures: open reduction and internal fixation with dorsal plating versus mini open reduction, percutaneous fixation, and external fixation.
- Is early internal fixation preferred to cast treatment for well-reduced unstable distal radial fractures?
- Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures: ORIF with a volar fixed-angle tine plate versus external fixation.
- Comparison of External and Percutaneous Pin Fixation with Plate Fixation for Intra-articular Distal Radial Fractures
- Functional outcomes for unstable distal radial fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation or closed reduction and percutaneous fixation. A prospective randomized trial.
- Distal Radius Fractures: Choice of Treatment Procedures
- Surgical treatment of distal radial fractures with a volar locking plate versus conventional percutaneous methods: a randomized controlled trial.
Historical References (Non Locking Technology)
Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults.
The surgical treatment of severe comminuted intraarticular fractures of the distal radius with the small AO external fixation device. A prospective three-and-one-half-year follow-up study..
Open reduction and internal fixation of comminuted, intraarticular fractures of the distal radius.
Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced, comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius.
Open treatment for displaced articular fractures of the distal radius.
Comminuted intraarticular fractures of the distal radius.
Displaced intraarticular fractures of the distal radius.
Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced, comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius.
An effective treatment of comminuted fractures of the distal radius.
Open treatment for displaced articular fractures of the distal radius.
Treatment of displaced articular fractures of the radius.
Open reduction and internal fixation for distal radius fractures
Factors affecting functional outcome of displaced intra-articular distal radius fractures.
The operative treatment of intraarticular fractures of the distal radius.
Indications and Techniques of Open Reduction. Internal Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures.
Treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius with plates.
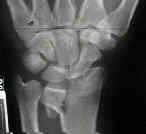
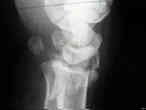
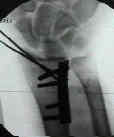
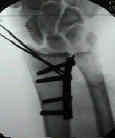
- Case Example: