- See: Ankle Sprains
- Discussion:
- indications:
- clinical symptoms are chief indications (radiographic findings may or may not correlate w/ the severity of the sprain and ankle dysfunction;
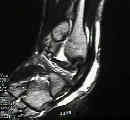
 - associated injuries:
- associated injuries:
- longitudinal tear of the peroneus brevis:
- contra-indications:
- fixed heel varus;
- obese patients;
- Radiographs: 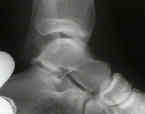
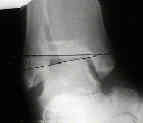
- Surgical Technique: 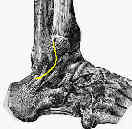
- curvilinear incision is made over distal anterior border of lateral malleolus;
- if peroneal tendon exploration is necessary, then consider a posterolateral longitudinal incision;
- beware of peroneal tendons inferiorly, sural nerve (which lies over the peroneal tendons), lesser saphenous vein (which can be ligated), and branches of the superficial peroneal nerve (intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve);
- after dissection procedes through subQ tissue, identify and preserve the inferior extensor retinaculum, which runs parallel to the CFL;
- this is mobilized for later attachment to the anterior edge of the fibula;
- identify the ATFL, which appears as a thickening in the anterior joint capsule;
- if it is torn, it is usually torn from the fibula;
- make anterior capsular incision along anterior margin of fibula down to its, distal tip, leaving a small cuff of tissue attached to the fibula (to facilitate later repair);
- identify the CFL at the inferior tip of the fibula;
- ankle is then placed in valgus and dorsiflexion, and the redundency of the ligament is assessed;
- sutures are passed thru the proximal edges of the ATFL and CFL;
- drill holes are made in the distal fibula;
- sutures are passed thru the drill holes, and are tied;
- the posterior edge of the extensor retinaculum is then opposed to the anterior edge of the fibula;
- this advancement of the retinaculum will help re-enforce the repair, limits the inversion, and addresses associated subtal instability;
- modified procedure using peroneus brevis:
- procedure results in significant loss of eversion and inversion;
- tendon harvest:
- procedure involves exposure of the peroneus brevis, while maintaining the integrity of the superior peroneal retinaculum;
- anterior third of the tendon is isolated distally and split from the distal position to the musculoskeletal junction;
- this tendon portion is transected at its proximal aspect;
- tendon anchorage:
- a drill hole is made through the distal fibula, and the split portion of the peroneus brevis is passed thru this hole;
- tendon is tensioned with the foot in mild plantar flexion and eversion;
- post op care:
- standard involves 6 weeks of casting, but there is some evidence that there are better functional results with 3 weeks of casting
- Outcomes:
- in the report by Messer TM, et al, the authors evaluated 22 patients with chronic lateral ankle instability who underwent surgical repair of their lateral ankle ligaments using suture anchors as part of the modified Brostrom procedure;
- at a mean follow-up of 34.5 months (minimum of 18 months), 20 patients (91%) reported a good or excellent functional outcome as assessed by the Karlsson and Peterson ankle function scoring scale;
- 14 of the 16 patients had no evidence of instability on exam or on stress radiographs;
- 1 patient had diminished sensation in the superficial peroneal nerve distribution;
- 5 of the 16 patients had generalized ligamentous laxity; none of these had an excellent result, and they had lower "Overall Satisfaction" scores (P = 0.013)
Sprained ankles. VI. Surgical treatment of "chronic" ligament ruptures.
The Modified Brostrom Procedure for Lateral Ankle Instability.
Ankle Instability Repair: The Brostrom-Gould Procedure
W.G. Hamilton Master Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery. The Foot and Ankle. Raven Press, Ltd. New York, 1994.
Reconstruction of the lateral ligaments of the ankle using a regional periosteal flap.
Clinical Instability of the Modified Brostrom Evans Procedure to Restore Ankle Instability.
Treatment of Ruptures of the Lateral Ankle Ligaments: A Meta-Analysis.
Outcome of the modified Brostrom procedure for chronic lateral ankle instability using suture anchors.
Comprehensive reconstruction of the lateral ankle for chronic instability using a free gracilis graft.
Long-term results after modified Brostrom procedure without calcaneofibular ligament reconstruction