- See: Radiographic Studies of the Foot and Ankle
- Static Films:
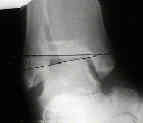
- os subfibulare:
- historically, this has been considered to be an accessory ossicle located just below the ditsal fibular epiphysis;
- it is distinguished from a fracture by its smooth borders, and by the fact that a fracture will preferentially involve the physis;
- there is some recent evidence to suggest that this structure may represent a nonunion of an avulsion frx from the fibula;
- patients may demonstrate ipsilateral ankle instability and absence of a similar ossicle on the contra-lateral foot;
- reference:
The symptomatic os subfibulare: Avulsion fracture of the fibula associated with recurrent instability of the ankle.
- Talar Tilt:
- stress test w/ ankle wts:
- examiner stabilizes the leg with one hand while inverting plantar flexed heel with the other hand;
- alternatively, place the patient's leg in the lateral position, hanging off the table;
- a strap is applied around the ankle which courses around the lateral side of the ankle;
- a 4 kg wt is then applied which forces the ankle into inversion and plantar flexion;
- other ankle may be used for comparison;
- line is drawn across the talar dome and tibial vault;
- degree of lateral opening angle is measured;
- normal tilt is less than 5 deg, others say an abnormal value is twice the angle of the normal ankle or over 9 deg;
- standing stress test:
- may be more sensitive than other stress tests;
- patient is stood on an inversion stress platform with the foot and ankle in 40 deg of plantar flexion and 50 deg of inversion;
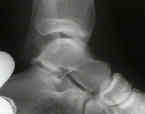 - Anterior Drawer Test:
- Anterior Drawer Test:
- abnormal anterior translation is between 5 to 10 mm, or 3 mm more than other side;
- External Rotation Stress Test:
- evaluates syndesmotic & deep deltoid ligament;
- on AP view differnece in width of superior clear space between medial and lateral side of the joint should be < 2 mm;
- these are static measurements of the talar position;
- in normal ankle, talus may tilt up to 5 deg w/ inversion stress;
- measurements of talar tilt using stress x-rays are used to evaluate lateral ligament stability;
- Arthrographic Studies of the Sprained Ankle:
- leakage of the dye thru a particular ligament or thru the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis will pin point structure torn;
- performed by inserting 22 gauge needle into the medial side of joint;
- extra articular dye anterior to the laterala malleolus is always associated with a rupture of ATFL;
- dye seen in peroneal sheath usually is caused by rupture of CFL;
- extension of contrast > 3.5 cm above joint is c/w ligamentous injury;
- arthrography needs to be performed within 1 week of injury or fibrin clots may seal any capsular tear;
- Decision Rules for Use of Radiography in Acute Ankle Injuries - Ottawa Rules
- Jama, March 3, 1993 - Vol 269, No. 9;
- ankle series are indicated if the patient has pain near the malleoli and one or more of the following:
- age 55 years or greater
- inability to bear wt immediately after injury & for 4 steps in ER.
- bone tenderness at the posterior edge or tip of either malleolus;
- foot series are indicated if the patient has pain in the midfoot and bone tenderness at:
- navicular bone
- cuboid
- base of the fifth metatarsal
- or is unable to bear weight

