- Discussion:
- calcaneofibular ligament is a extra-articular round and cordlike ligament which connnects tip of distal fibula to small tubercle on posterior & lateral aspect of calcaneus;
- crosses two joints, talocrural and the talocalcaneal;
- 2 cm long, 5 mm wide, and 3 mm thick;
- calcaneal attachment of calcaneofibular lig is 13 mm from subtalar joint, & that insertion of anterior talofibular ligament onto talus is 18 mm posterior to subtalar joint;
- calcaneofibular lig attaches posteriorly on calcaneus to form 133-deg angle w/ fibula when ankle is in neutral dorsiflexion-plantar flexion
- it is in close contact with medial peroneal sheath, but is not associatted with either the ankle capsule or peroneal tendon sheath;
- Function:
- it is lax in normal, standing position due to relative valgus orientation of calcaneus;
- it acts primarily to stabilize sub-talar joint & limit inversion;
- this ligament is extra-articular but it has an intimate connection to overlying peroneal-tendon sheath;
- calcaneofiblar ligament may be lax until supination force is applied;
- greatest strain occurrs when inversion moment is applied w/ ankle in dorsiflexion;
- because of its unique anatomical orientation, calcaneofibular ligament also has major role in stabilization of subtalar joint;
- isolated rupture of the calcaneofibular ligament probably does not cause demonstrable ankle laxity;
- Exam:
- inversion (supination) test;
- w/ ankle in plantarflexion: evaluates anterior talofibular ligament;
- in neutral / slight dorisflexion: evaluates calcaneofibular ligament;
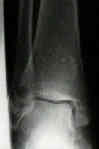
- talar tilt:
- talar instability is assessed w/ talar tilt test, in which angle formed by tibial plafond & talar dome is measured as inversion force is applied to hindfoot;
- talar tilt test is useful for evaluation of combined injury of both anterior talofibular & calcaneofibular ligament;
- talar tilt to ranges from 0 to 23 degrees in normal ankles, while but normal ankles tend to have < 5 degrees of talar tilt;
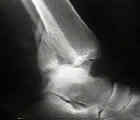
- Arthrography:
- w/ ankle arthrography, contrast medium often fails to enter peroneal sheath, despite operatively proved tears of calcaneofibular ligament;
- technique of peroneal tenography was developed has proved to be more accurate in the diagnosis of disruption of calcaneofibular ligament;
- leakage of the dye through a particular ligament or thru the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis will pin point structure torn;
- performed by inserting 22 gauge needle into the medial side of joint;
- extra articular dye anterior to the laterala malleolus is always associatted with a rupture of ATFL;
- dye seen in peroneal sheath usually is caused by rupture of CFL;
- extension of contrast > 3.5 cm above joint is c/w ligamentous injury;
- arthrography needs to be performed within 1 week of injury or fibrin clots may seal any capsular tear

