- Anatomy:
- origin: distal 2/3 of the lateral surface of the body of fibula and the adjacent intermuscular septa;
- insertion: tuberosity on lateral side of proximal end of 5th metatarsal;
- action:
- plantar flexion and eversion of the foot at the ankle;
- gives lateral stability to the ankle;
- primarily active during the stance phase of gait;
- nerve supply:
- peroneal, S1 > L5, L4; (see innervation)
- synergists: gastrocnemius, soleus, peroneus longus.
- Pathologic Conditions:
- peroneal tendon disruption:
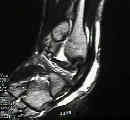
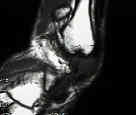
- peroneus brevis tear:
- longitudinal tears of the peroneus brevis are associated w/ ankle sprains;
- look for tendon tear at the level of the distal fibula;
- persistent swelling along the peroneal tendon sheath is a reliable sign for peroneus brevis tendon tear;
- this injury tends to occur from peroneal tendon subluxation over the posterolateral edge of the fibula;
- inciting cause is incompetence of the superior peroneal retinaculum;
- this allows subluxation of the peroneal tendons and mechanical attrition of the peroneus brevis tendon against the posterior ridge of the fibula;
- treatment: needs to address the tear and the peroneal subluxation;
- w/ damage of less than 50% tendon substance, consider tendon debridment;
- w/ damage of more than 50% of the tendon cross sectional area, consider excision of the damaged segment and tenodesis to the peroneus longus;
- Peroneus Brevis Muscle Flap:
- see: soft tissue coverage of the leg;
- peroneus brevis muscle is the most useful flap to reconstruct small defects of the distal third of the lower leg;
- located in lateral compartment & supplied by peroneal artery, transposition to small distal third wounds is feasible;
- vertical incision over the fibula from the mid calf to the lateral malleolus is performed;
- beneath the peroneus longus, the peroneus brevis is separated from EDL anteriorly and the soleus posteriorly;
- dissection is continued proximally to the proximal third of muscle;
- more proximal dissection risks injury to the vascular pedicle and should be avoided;
- flap can then be transposed anteriorly
Peroneus brevis tendon tears: pathophysiology, surgical reconstruction, and clinical results.
Static or dynamic repair of chronic lateral ankle instability. A prospective randomized study.
The peroneus quartus muscle. Anatomy and clinical relevance.