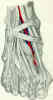
- Origin:
- lateral condyle of the tibia, head and proximal 3/4 of the anterior surface on the body of the fibula, proximal portion of interosseus
membrane, deep fascia and intermuscular septa;
- Insertion:
- divides into 4 tendons after passing under the extensor retinaculum;
- unlike the EDC, there is no dorsal insertion of the EDL to the proximal phalanx;
- instead, the proximal phalanx is suspended by the EDL and extensor sling;
- extensor sling (saggital bands) span either side of the tendon and are anchored to the volar plate of the MTP joint;
- tendon then divides into 3 slips;
- central slip inserts into base of middle phalanx;
- two lateral slips unite and insert onto distal phalanx;
- Nerve supply: peroneal, L5 > L4, S1; (see innervation)
- Action:
- extends toes at the foot;
- dorsiflexion and everts foot at the ankle.
- main action of the EDL is to dorsiflex the phalanx;
- it is able to dorsiflex the PIP joint only when the phalanx is in a neutral or flexed position;
- Synergist: Extensor Digitorum Brevis