- Examination of Patellofemoral Joint
- exam considerations:
- generalized hyperlaxity
- femoral anteversion
- vastus medialis obliquus atrophy
- genu valgum
- external tibial torsion
- patellar dysplasia
- trochlear dysplasia
- patella alta
- pes planus
- Radiographic Features: (see: radiographic evaluation of the knee)
- lateral view
- look for patella alta and/or patellar osteochondral fracture;
- axilla view and merchant technique: (looking for trochlear dysplasia)
- if patella is well centered in groove at 30 deg of flexion, tracking is normal;
- w/ h/o previous patellar dislocation, look for concomitant medial patellar facet fractures;
- because increased flexion results in reduction of subluxated patella, x-rays be obtained w/ in 20 and 45 degrees of flexion;
- note that in children, there will always be an apparent osseous patellofemoral dysplasia, but the cartilaginous border is thicker than seen in adults;
- references:
- Radiological measurements in patellofemoral disorders. A review.
- Radiographic analysis of patellar tilt.
- Radiology of postnatal skeletal development. X. Patella and tibial tuberosity.
- CT scan:
- CT scanning should be reserved for those difficult cases in which plain radiographs are indeterminate;
- may reveal occult osteochondral fractures;
- may reproduce patellofemoral relationships including normal alignment, lateral patellar tilt, and patellar subluxation;
- CT images are taken thru the first 45 deg of knee flexion;
- taken at 0 deg, 15 deg, 30 deg, and 45 deg of flexion;
- use the posterior condyles as a reference line for determining tilt;
- MRI Findings:
- shows bone bruises in the medial aspect of the patella and the lateral aspect of the lateral femoral condyle
- references:
- Acute lateral patellar dislocation at MR imaging: injury patterns of medial patellar soft-tissue restraints and osteochondral injuries of the inferomedial patella.
- A systematic approach to magnetic resonance imaging interpretation of sports medicine injuries of the knee.
- Non Operative Treatment:
- acute dislocation:
- if patient presents w/ the patella unreduced, then reduction is effected by flexing the hip and then applying medial stress while gradually extending the knee;
- first episode of traumatic lateral patellar dislocation or subluxation is treated non operatively unless there is a loose fracture fragment in the joint;
- a period of immobilizaiton may be needed to allow medial restraints to heal;
- unfortunately, up to 50% of pts will have recurrent episodes of patellofemoral instability, and, in this group, surgical correction is indicated;
- w/ patellar subluxation, treatment involves quadriceps strengthening exercises;
- patellar knee sleeves may be of some use, however, prospective studies have failed to demonstate their effectiveness;
- references:
- First-time Traumatic Patellar Dislocation: a Systematic Review.
- Acute Patellar Dislocation in Children and Adolescents: a Randomized Clinical Trial
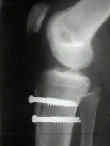
- Surgical Treatment:
- in child, patellar subluxation or dislocation often requires arthroscopy;
- if osteochondral lesions are encountered, then reduction and pinning is indicated;
- factors which disfavor soft tissue procedures:
- generalized hyper-elasticity
- patellofemoral dysplasia
- increased Q angle (lateralized tibial tubercle)
- treatment options:
- soft tissue procedures:
- medial patello-femoral ligament repair
- lateral retinacular release:
- indicated only in individuals demonstrating tightness of lateral retinaculum.
- patella tilt test indicates tightness of lateral retinaculum.
- especially poor results are noted when a lateral retinacular release is performed in patients w/ multidirectional patellar instability;
- ref: Arthroscopically Assisted Medial Reefing Without Routine Lateral Release for Patellar Instability.
- osseous realignment:
- distal realignment procedures
Preliminary experience with a method of quadricepsplasty in recurrent subluxation of the patella.
Proximal and distal reconstruction of the extensor mechanism for patellar subluxation.
Treatment of acute patellar dislocation.
Surgical treatment of recurrent dislocation of the patella.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Patellofemoral Kinematics with Weight-Bearing.