- See: Anterior Approach to Shoulder and Synthes Proximal Humerus Products
- Operative Treatment Options:
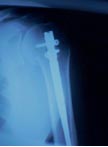
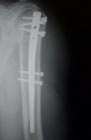
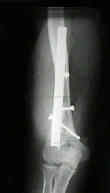
- Lateral Plating (Locking Plating):
- Percutaneous Pinning
- Screw Tension Band Technique:
- reduction:
- in some cases cancellous bone from the humerus head is removed to allow better impaction;
- insert 4.5 or 6.5 mm cancellous lag screw from the shaft up into the head, just shy of the subchondral bone;
- following screw insertion, figure of 8 tension band wiring (consider No 5 Ethibond) is passed
around the rotator cuff origin on greater tuberosity to a drill hole made in the humeral shaft; 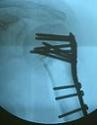
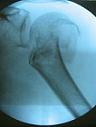
- a second wire is inserted thru both the lesser and greater tuberosities;
- reference:
- Internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the screw-tension band technique.
- Shoulder Replacement:
- need for revision is significantly higher in patients who underwent hemiarthoplasty for trauma
rather than for rheumatoid arthritis;
- upto one half of younger patients undergoing hemiarthroplasty will have subjective
or objective unsatisfactory results;
- technical considerations with fracture:
- IM nailing:
- main disadvantage of IM nailing is that shoulder adduction is required for nail entry into the medullary canal where as
shoulder abduction is often necessary for fracture reduction;
- Is antegrade nailing a proper option in 2- and 3-part proximal humeral fractures?
- Complications:
- non-union:
- avascular necrosis:
- Avascular necrosis of the humeral head treated by core decompression. A retrospective review.
- Vascularity of the humeral head after proximal humeral fractures. An anatomical cadaver study.
- malunion:
- need to categorize the malunion w/ functional and anatomic characteristics;
- look for malposition of the tuberosities, incongruity of the articular surface, malalignment of the articular segment, soft
tissue contractures, rotator cuff tears, instability ect;
- w/ internal rotation contracture, Z lengthening of the subscapularis may be required;
- w/ operative correction of malunion, a good postoperative result requires correction of both soft tissue and osseous
abnormalities;
- references:
- Operative treatment of malunion of a fracture of the proximal aspect of the humerus.
- Humeral tuberosity fractures. Evaluation by CT scan and management of malunion. Morris ME et al. Orthop Trans.
1987;11:242.
- pulmonary embolism:
- Pulmonary embolism after operative treatment of proximal humeral fractures
- screw cut out:
- Fracture Displacement and Screw Cutout After Open Reduction and Locked Plate Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures
The difficult proximal humerus fracture: tips and techniques to avoid complications and improve results.
Clinical use of the olecranon-manubrium percussion sign in shoulder trauma.
A posterior surgical approach to the proximal part of the humerus.
Internal fixation techniques for proximal humeral fractures.
Displaced proximal humeral fractures. Selecting treatment, avoiding pitfalls.
Proximal humeral fractures. Management techniques and expected results.
The two-part proximal humeral fracture: a review of operative treatment using two techniques.
Proximal humeral fractures revisited.
Treatment of displaced proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients.