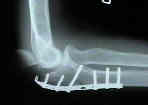
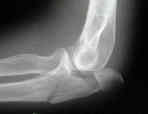
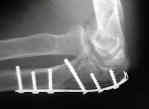
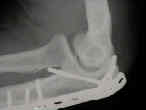
- Discussion: (see olecranon frx menu)
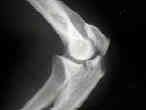
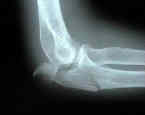
- indicated for comminuted olecranon frx and frx which occur at or distal to the coronoid process;
- if frx extends distally past midpoint of trochlear notch, it no longer represents only a disruption of the triceps
mechanism but also comprimises the stability of elbow in withstanding varus & valgus forces / in this case,
plate fixation is required;
- these fractures will be subjected to increase rotational forces that may cause tension band fixation to fail;
- distance between coronoid process & olecranon must not be shortened by compression of the comminuted fragments;
- always explain to patient beforehand that plate may require future removal;
- note that in the study by Hume MC and Wiss DA (1992), plate fixation yielded significantly better clinical results than TBW;
- comminuted olecranon fractures are another indication for plate fixation;
- associated coronoid process fracture
- coronoid fracture is exposed by reflexion of the olecranon fracture and attached triceps proximally;
- direct exposure is achieved working through the fracture site;
- coronoid is stabilized with w/ screws w/ the heads screwed down to the level of the fracture site;
- the main olecranon fracture is then reflected back down, reduced and fixed in the usual manner;
- Olecranon fractures. A clinical and radiographic comparison of tension band wiring and plate fixation.
- Implants:
- w/ pts < sixty years old, consider 3.5-mm AO DCP contoured to fit fractured olecranon following reduction;
- this neutralizes forces across coronoid frx from tip of olecranon to shaft;
- alternatively use or 3.5 pelvic reconstruction plate;
- one third tubular is another alternative in compliant patients;
- if 3.5 DCP or 3.5 pelvic recon plate is to be used, a bending press will be required for contouring;
- Surgical Approach:
- reduction:
- reduction of olecranon frx is easiest w/ elbow in extension which relaxes the pull of the triceps muscle;
- once reduced, apply towel clamp to frx site;
- consider placing the tips of the two towel clamps in tension band holes;
- ref: Impact of olecranon fracture malunion: Study on the importance of PUDA (Proximal Ulna Dorsal Angulation).
- initial fixation:
- frx of olecranon which is distal to midpoint of trochlear notch, if not comminuted, such as oblique frx, is first stabilized w/ lag screws;
- K wires are not enough for lateral support;
- to overcome valgus/varus instability distal frxs, need to be supplemented w/ plate, even if fixed w/ lag screws,
- What Is the Ideal Starting Point for an Olecranon Screw? An Anatomic Cadaveric Study
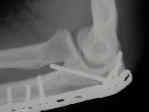
- Plate Fixation: (3.5-mm AO DCP)
- contour the dorsally applied plate to allow the fully threaded proximal screw to be inserted at 90 deg to the more distal screws;
- the next two distal screws can usually be placed in the proximal fragment, and should be aimed to avoid the proximal screw;
- the next screw should be placed in compression mode;
- if the coronoid process is fractured, skip the overlying screw hole and apply compression to the next most distal screw hole;
- subsequently, a lag screw can be inserted through the plate (neutral mode) to grab the coronoid fracture fragment;

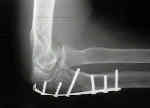
- Plate Fixation for Olecranon Nonunion: (from Danziger and Healy (1992))
- 3.5 DCP is contoured to the proximal fragment;
- K wires are used to achieve provisional fixation;
- plate is secured to proximal frx fragment;
- ensure that the plate does not block full extension;
- external compression device is applied, and provisional fixation is removed;
- lag screws are applied both proximal and distal to the frx line in divergent positions;
- the proximal lag screw is directed across the frx to the coronoid process;
- the distal lag screw is directed across the frx to the olecranon tip;
- Complications:
- inadequate fixation: the proximal fragment was held w/ only a hook plate
- references:
- Experience with the McAtee olecranon device in olecranon fractures.
- The use of the Zuelzer hook plate in fixation of olecranon fractures.
- Displaced olecranon fractures in adults. Biomechanical analysis of fixation methods.
- Methods of fixation of olecranon fractures. An experimental mechanical study.
- Olecranon fractures. A clinical and radiographic comparison of tension band wiring and plate fixation.
- An off-loading triceps suture for augmentation of plate fixation in comminuted osteoporotic fractures of the olecranon.
- Olecranon fractures. A clinical and radiographic comparison of tension band wiring and plate fixation.
- Tension Band Plating for NonUnion of Proximal Ulna and Olecranon. Healey WL. Tech Orthop. 1991;6:51-54.
- Posterior olecranon plating: biomechanical and clinical evaluation of a new operative technique.