- see: Stress Frx Menu
- proximal 1/3 of tibia is most common site for tibial stress frxs in adolescents, but in runners tibial stress frx occur near junction of middle and distal thirds;
- tibia is the most frequent stress fracture location in most series in both athletes and modern military training;
- diff dx:
- exertional compartment syndrome
- shin splints:
- pain is located in posterior mid to distal 1/3 of tibia which is related to periostitis at origin of tibialis posterior;
- exam is notable for local tenderness w/ pain on resisted plantar flexion and inversion;
- fascial hernias;
- ewing's sarcoma;
- osteoid osteoma;
- prognosis:
- tibial stress frxs may occassionally result in non union even after 4 to 6 months of conservative care;
- it is not unusual for stress fracture to persist for over one year;
- posteromedial stress frx
- occurs on the compression side of the tibia and has a good prognosis with non operative treatment;
- anterolateral stress frx:
- occurs on the tension side of the fracture and may be associated with prolonged non union;
- the prognosis for healing is worse when there are multiple anterior black lines;
- midanterior tibial stress fractures may also require long-term nonoperative treatment;
- Exam:
- point tenderness over an area of induration;
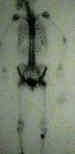
- Radiographs: (bone scan)
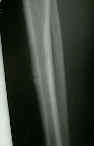
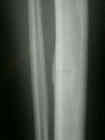 ***
*** 

- Treatment:
- patients require reduction in activity and in some cases require casting;
- external bone stimulator may improve the non operative care of these patients;
- in chronic cases, consider IM nailing of the tibia fracture;
- references:
- Intramedullary nailing for chronic tibial stress fractures. A review of five cases.
- Chronic anterior midtibial stress fractures in athletes treated with reamed intramedullary nailing
Stress fractures of the medial tibial plateau.
Stress fractures of the proximal tibia in runners.
Management of knee osteoarthritis presenting with tibial stress fractures
Nonunion of tibial stress fractures in patients with deformed arthritic knees. Treatment using modular total knee arthroplasty
Proximal tibial stress fracture associated with mild osteoarthritis of the knee: case report.
Proximal tibia stress fracture caused by severe arthrosis of the knee with varus deformity
A case of bilateral stress fractures in an old woman: three years of pain.
Stress fractures of the medial tibial plateau
Surgical versus conservative treatment for high-risk stress fractures of the lower leg (anterior tibial cortex, navicular and fifth metatarsal base): a systematic review.
An analysis of the biomechanical mechanism of tibial stress fractures among Israeli infantry recruits. A prospective study.
Clinical significance of nonfocal scintigraphic findings in suspected tibial stress fractures.
Medial tibial pain. A prospective study of its cause among military recruits.
Stress fractures in athletes. A study of 320 cases.
Epidemiology and site specificity of stress fractures.
Nonunion of a distal tibial stress fracture associated with vitamin D deficiency: a case report.

