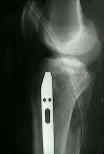
 - Discussion:
- Discussion:- history: Intramedullary nailing in fracture treatment: History, science and Küntscher's revolutionary influence in Vienna, Austria
- healing and prognosis of tibia fracture
- PreOp Planning:
- Contra-indications:
- open growth plates; (pediatric tibial frx);
- fractures w/ 4 cm of the ankle joint;
- previous application of external fixator (relative contraindication - controversial);
- proximal fourth tibial fractures (relative contraindication - controversial)
- Soft tissue injury:
- Open tibial frx (Gustillo classification):
- Reconstruction for leg defects:
- Comminution: (see Winquist classification):
- Technique of IM Nailing:
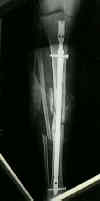
- Outcomes for IM Nails vs Other Treatment Methods:
- external fixation vs IM nailing for tibial frx
- Klemm and Borner (1986);
- 401 tibial fractures: 308 closed, 93 open grade I (delayed nailing)
- 81% of frx were considered unstable to shortening or rotation;
- 94% w/ good to excellent results, 2.2% deep infection
- Puno, et. al. (1986)
- 201 tibial fractures: AO type reamed slotted tibial nail w/ closed technique versus closed
reduction w/ cast application;
- IM nail: 98% union rate (no malunions), 3.3% infection rate;
- cast immobilzation:
- 90.1% unions, 4.3% malunions, 1.4% infections;
- initially 13% of fractures lost the reduction and required operation;
- Bone and Johnson
- 76 primary fractures and 36 2ndary fractures (exfix/closed failures)
- using AO or Grosse-Kemph IM Nailing;
- union rate: 97% for both groups;
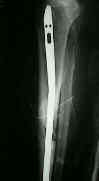
- time to union: primary group: av 17.8 weeks vs secondary group: av 21.6 weeks
- infection: 9% - mostly pts rx'ed w/ open procedures or open frx;
- Bone, et al (1997)
- retrospective study of 99 patients w/ closed tibial shaft fractures treated either w/ cast or IM nail;
- avg. time to union w/ IM nail was 18 weeks vs 26 weeks with a cast;
- non-union occur in 2% of IM nail patients vs 10% in casted patients;
- 26 of 47 patients requested that the IM nail be removed;
- IM nail group had higher Iowa knee and ankle evaluation rating system scores than casted group;
- references:
- Treatment of tibial fractures by reaming and intramedullary nailing.
- Interlocking nailing of complex fractures of the femur and tibia
- Critical analysis of results of treatment of 201 tibial shaft fractures
- Displaced isolated fractures of the tibial shaft treated with either a cast or IM nailing. An outcome with analysis of matched pairs of patients.
- The use of the Lottes nail in the treatment of closed and open tibial shaft fractures.
- Conservative management or closed nailing for tibial shaft fractures. A randomised prospective trial.
- Locked intramedullary nailing for displaced tibial shaft fractures
- Infection after intramedullary nailing of the tibia. Incidence and protocol for management.
- Diagnosis and management of infection after tibial intramedullary nailing.
- Unstable fractures of the tibia treated with a reamed intramedullary interlocking nail.
- Radiographic analysis of tibial fracture malalignment following intramedullary nailing.
- Comparison of functional bracing and locked intramedullary nailing in the treatement of displaced tibial shaft fractures.
- Use of IM Nails in Open Fractures: (see open tibial frx and exchange nailing)
- references:
- The use of the Lottes nail in the treatment of closed and open tibial shaft fractures.
- Locked intramedullary nailing of open tibial fractures.
- Treatment of open fractures of the tibial shaft with the use of interlocking nailing without reaming.
- Infection after intramedullary nailing of the tibia. Incidence and protocol for management.
- Diagnosis and management of infection after tibial intramedullary nailing.
- Prospective study of union rate of open tibial fractures with locked unreamed intramedullary nails.
- Closed intramedullary tibial nailing: its use in closed and type I open fractures.
- Lower infection rate after interlocking nailing in open fractures of the femur and tibia.
Treatment of infected non-unions and segmental defects of the tibia with staged microvascular muscle transplantation and bone-grafting.
Locked nailing for nonunion of the tibia.
Open intramedullary nailing and bone-grafting for non-union of tibial diaphyseal fracture.
The use of Ender nails in fractures of the tibial shaft.
The treatment of 143 tibial shaft fractures by Ender's nailing and early weight-bearing.
Flexible medullary nailing of acute tibial shaft fractures.
Validation of a standardised gait score to predict the healing of tibial fractures

