- See:
- Casting of Tibial Fractures
- Distal Tibial Fracture
- Intercondylar Eminence Fracture
- Proximal Tibial Physeal Fractures
- Proximal Tibial Metaphyseal Fractures
- Tibial Tuberosity Fractures
- Pediatric Ankle and Distal Tibia Fractures:
- Triplane Fracture
- Shortening:
- pediatric tibial frxs do not have much potential for overgrowth, hence, it is essential to to maintain frx out to length;
- when shaft of tibia & fibula are fractured, major problem, is shortening;
- w/ fibula no longer intact, long flexor muscles tend to produce a valgus deformtiy at the fracture site;
- acceptable shortening:
- 1 to 5 yrs of age: 5 - 10 mm
- 5 to 10 yrs of age: 0 - 5 mm
- Axial Malalignment:
- frxs of tibia and fibula do not have much poential to correct axial malalignment;
- acceptable reduction:
- less than 10 deg of recurvatum;
- less than 5 deg of varus or valgus angulation;
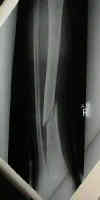
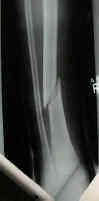
- case example:
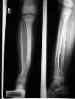
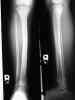
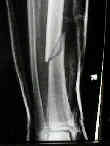
- this child sustained a distal shaft frx of both the tibia and fibula;
- the frx was in valgus, and even after reduction, slight valgus remained;
- despite the usual teaching that the tibia has poor remodeling potential, this child went on to heal w/ little residual deformity;
- Treatment:
- cast application:
- frx of tibial & fibular shafts in children are usually uncomplicated and can be treated by closed reduction and long leg cast application;
- flexion to 45 deg will facilitate rotational control of the fracture;
- w/ a recurvatum deformity, the foot should be placed in slight plantar-flexion: neutral dorsiflexion will increase frx recurvatum in an unstable frx;
- in older children, the long leg cast can be converted to a patellar tendon bearing cast after a period of 3 weeks;
- intramedullary nails: (synthes technique manual)
- references:
- Intramedullary Kirschner wiring for tibia fractures in children.
- Operative Treatment of Tibial Fractures in Children: Are Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nails an Improvement Over External Fixation?
- Intramedullary Flexible Nail Fixation of Unstable Pediatric Tibial Diaphyseal Fractures.
- Immediate Intramedullary Flexible Nailing of Open Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
- The incidence of compartment syndrome after flexible nailing of pediatric tibial shaft fractures
- Outcomes Using Titanium Elastic Nails for Open and Closed Pediatric Tibia Fractures
- external fixation:
- External fixation of lower limb fractures in children.
- Compartment Syndrome:
- Acute Compartment Syndrome in Children and Teenagers with Tibial Shaft Fractures: Incidence and Multivariable Risk Factors
- Varus Mal-Reduction:
- oblique isolated frx of tibial shaft (w/ fibula intact) may drift into varus because of pull of long flexors of the toes & ankle;
- varus mal-reduction is addressed by placing knee in flexion & ankle in mild plantar flexion during first 1-2 weeks of immobilization;
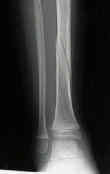
- case example:
- this 13-year-old female drifted into varus, despite attempts to maintain the reduction w/ cast wedging;
- in this case, the patient and physician elected to have plate fixation;
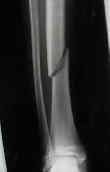
- Spiral Fracture:
- case example: residual varus after casting:
Open fractures of the tibia in children.
Ipsilateral fractures of the femur and tibia in children and adolescents.
Functional fracture-bracing of long-bone fractures of the lower extremity in children.
Residual bone-mineral density and muscle strength after fractures of the tibia or femur in children.
Tibial spine fractures in children.
Current Concepts Review. Fractures about the Knee in Children.
Physeal arrest about the knee associated with non-physeal fractures in the lower extremity.
Remodeling of tibial fractures in children younger than 12 years.