- distal radius fracture w/ dislocation of radiocarpal joint;
- most common frx dislocation of the wrist joint;
- comminuted frx of distal radius may involve either anterior or posterior cortex and may extend into the wrist joint;
- frx dislocation or subluxation in which the rim of distal radius, dorsally or volarly is displaced with the hand and carpus;
- it often occurs along with a radial styloid frx;
- it differs from Colles' or Smith's Fracture in that the dislocation is the most striking radiographic finding;
- in most cases, marginal frag is smaller than in anterior injury & often involves medial aspect where EPL crosses distal radius;
- Radiographs: 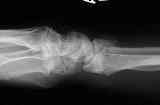
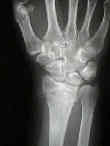
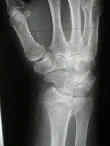
- Non Operative Treatment:
- many of these frxs will fail nonoperative treatment;
- manipulative reduction is same as for Colles Fracture;
- stability of reduction of dorsal Barton frx is best obtained with wrist extension to take advantaage of intact volar carpal ligament;
- immobilization for 6 weeks in short arm plaster cast;
- Operative Treatment:
- is best treated by closed reduction, application of external fixation, followed by percutaneous pin insertion;
- if reduction is not anatomic, fraying of the tendon at this level may to late rupture;
- tendency to redisplace may require ORIF through dorsal approach
- ref: Case-control study on T-shaped locking internal fixation and external fixation for the treatment of dorsal Barton's fracture
Anterior and posterior marginal fracture-dislocations of the distal radius. An analysis of the results of treatment.
Barton's fractures - reverse Barton's fractures. Confusing eponyms.

