- See: X-rays of the Foot
- Radiographs:
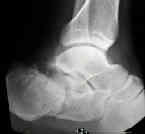
- broden's view:
- dorsoplantar (AP):
- delineates calcaneocuboid joint
- demonstrates amount of lateral spread of calcaneus
- demnstrates subluxation of talonavicular joint;
- frx lines will extend into anterior body of calcaneus, deforming articulation, and severe displacement of calcaneal frx may be assoc w/ talonavicular subluxation;
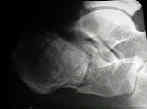
- lateral view:
- decrease in Bohler's angle;
- incongruity and loss of height of posterior facet;
- increase in angle of Gissane;
- demonstrates joint depression & tongue type frx;
- lateral x-rays provide minimal information about subtalar joint;
- direction of the primary fracture line is typically vertical where as secondary posterior fracture line is transversely oriented;
- harris beath view - axial calcaneal projection
- obtained by angling beam 45 (10 to 45 deg) from behind leg, & centering it on posterior portion of sub-talar joint;
- demonstrates tuberosity, body, sustentaculotalar joint, & posterior facet of the calcaneus;
- amount of widening of the heel
- impingement of lateral frag on peroneal space & lateral malleolus;
- degree of overiding of superomedial fragment on psoterolateral fragment, & degree of comminution & displacement of subtalar fracture fragments;
- axial or tangential radiograph is helpful in assessing direction of primary frx line, involvement of posterior talocalcaneal joint, lateral comminution of frx, & spreading of the heel
- CT Scan for Calcaneal Fractures
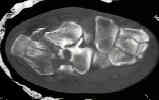
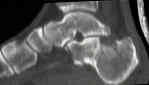
Radiologic aspects of calcaneal fractures in childhood and adolescence.

