- Discussion:
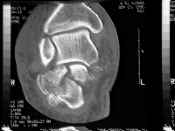
- demonstrates intra-articular extension of frx
- degree of comminution of posterior facet;
- calcaneocuboid joint;
- impingement of lateral border of calcaneus on lateral malleolus and entrapment of tendons or nerves can be demonstrated;
- latter is best seen with the soft-tissue window examination;
- Axial Images:
- pt extends hips & knees, & second scout film is obtained for transverse CT scanning (90 deg to the coronal view and parallel to the long axis of the foot);
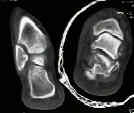
- transverse plane views provide good visualization of talo-navicular & calcaneocuboid joints, anteroinferior aspect of the posterior facet, the sustentaculum tali, and the lateral calcaneal wall;
- use axial images to help determine how much of the posterior facet remains attached to the sustentaculum tali;
- Coronal Images:
- position pt w/ hip and knees flexed, w/ feet taped together;
- lateral x-ray (scout film) is obtained & position is modified until coronal sections are perpendicular to posterior facet;
- usually needs to be angled 30 deg;
- coronal images are taken in 3 mm slices from posterior calcaneus to the navicular;
- determine location of primary frx line, as being intra- or extra articular at the posterior articular facet;
- useful in visualizing talocalcaneal facets, is usually performed w/ patient supine and the knees flexed;
- Sander's Classification:
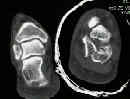
- choose the coronal CT image that shows the posterior facet in widest profile;
- mark two verticle lines to divide the posterior facet into three equal secitons; (hence: A-Lateral, B-Central, Medial-C);
- the final line marks the verticle border of the sustentaculum;
- fractures which lie in the medial zones will be more difficult to visualize and hence, will be more difficult to achieve primary repair;
- type II fractures: two part;
- type III fractures: three part fracture w/ depression of posterior facet;
- type IV: Severely Comminuted
Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system.
CT measurement of the calcaneal varus angle in the normal and fractured hindfoot.
Computed tomography of calcaneal fractures: anatomy, pathology, dosimetry, and clinical relevance.
Computerized tomographic analysis of acute calcaneal fractures.