- Discussion: 
- rotator cuff anatomy
- frequency of tear
- diff dx of cuff tears; (partial rotator cuff tear)
- etilogy of tear
- ref: Association between alcohol consumption and rotator cuff tear
- how do RTC tears heal?
- Shoulder Exam: 
- impingement sign and test:
- it is essential to document ROM deficits, since rotator cuff repair would not be expected
to yield a good outcome in the face of fixed shoulder contractures;
- Radiographic Findings:
- scapular outlet view
- 30 deg caudal tilt view AP view
- arthrography
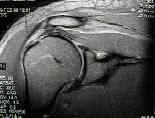
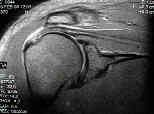
- MRI of Shoulder: Coronal Oblique View of Shoulder
- Surgical Management:
- assessment of cuff tear / mobilization of cuff / restoration of the foot print
- note intervening bare area between the articular margin and the infraspinatus and teres minor
- partial rotator cuff tear:
- management of massive rotator cuff tear
- tears due to impingement and trauma: (see: impingement syndrome)
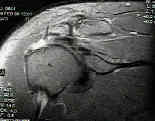
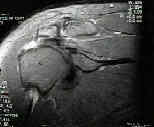
- arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
- arthroscopy (arthroscopic acromioplasty) followed by rotator cuff repair
- allows accurate assesment of rotator cuff tear;
- look for hypervascularity at the base of the biceps tendon as well as fraying of the cuff just lateral to the biceps tendon;
- does not require elevation of the deltoid off the acromioplasty;
- allows a more lateral incision, directly over the rotator cuff tear, (avoid deltoid detachment);
- w/ restricted motion, consider arthroscopic capsular release prior to rotator cuff tear;
- open rotator cuff repair and open acromioplasty
- concomitant procedures:
- biceps tenodesis;
- distal clavicle excision (w/ concomitant arthrosis)
- ref: The influence of distal clavicle resection and rotator cuff repair on the effectiveness of anterior acromioplasty.
- precautions:
- rotator cuff repair should not be performed in the face of a fixed contracture;
- consider aggressive PT to restore motion or arthroscopic release of rotator interval (for loss of external rotation in
adduction) or release of the posterior capsule (for loss of internal rotation);
- tears due to instability:
- requires anterior reconstruction in addition to rotator cuff repair;
- ref: Occult anterior subluxations of the shoulder in noncontact sports.
- Complications:
- Failed Acromioplasty / Rotator Cuff Surgery:
- Fatty Muscle Atrophy:
- Muscle regeneration following repair of the rotator cuff
- Captured Shoulder:
- refers to restrictive subdeltoid adhesions which develop following surgery and which limit ROM;
- may occur in about 5% of patients;
- treatment relies arthroscopic lysis of adhesions;
- references:
- Failed Repair of the Rotator Cuff. Evaluation and Treatment of Complications.
- Superior Humeral Dislocation: A Complication Following Decompression and Debridement for Rotator Cuff Tears.
- Operative Treatment of failed repairs of the rotator cuff.
- Captured Shoulder: a complication of rotator cuff surgery.
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................