 - Discussion:
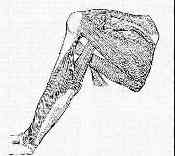
- Discussion: - rotator cuff anatomy
- frequency of tear
- diff dx of cuff tears
- etilogy of tear:
- impingement syndrome: (75%)
- shoulder instability (anterior or multi-directional) (15%) (should be considered in any young active patient);
- trauma:
- occurs in 10% of patients;
- note that a displaced greater tuberosity frx is a RTC tear equivolent;
- by definition, partial tears involve 50% or more of the tendon;
- in the study by Weber SC (1999), 32 patients with significant partial-thickness rotator cuff tears were treated with debridement and acromioplasty versus 33 patients who were with mini-open repair;
- 88% of tears were on the articular sidee;
- acromiplasty and debridement group:
- significant number of the arthroscopic group had fair results by UCLA score criteria;
- 3 patients reruptured the remaining cuff later despite adequate acromioplasty;
- healing of the partial tear was never observed at second-look arthroscopy;
- acromioplasty alone did not prophylactically prevent rotator cuff tear progression;
- the good results of arthroscopic treatment of significant partial-thickness tears deteriorated with time;
- open repair group:
- although postoperative pain was significantly greater and recovery slower with open repair, no patient was reoperated on and rerupture of the repair did not occur;
 - Shoulder Exam:
- Shoulder Exam:- impingement sign and test:
- it is essential to document ROM deficits, since rotator cuff repair would not be expected to yield a good outcome in the face of fixed shoulder contractures;
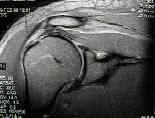
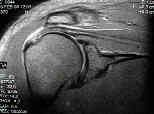
- Radiographic Findings:
- scapular outlet view
- 30 deg caudal tilt view AP view
- arthrography
- MRI of Shoulder: Coronal Oblique View of Shoulder
- Surgical Treatment:
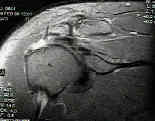
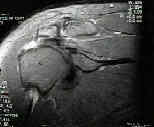
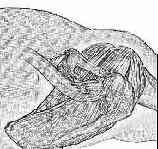
- arthroscopy (arthroscopic acromioplasty) followed by rotator cuff repair
- allows accurate assesment of rotator cuff tear;
- look for hypervascularity at the base of the biceps tendon as well as fraying of the cuff just lateral to the biceps tendon;
- does not require elevation of the deltoid off the acromioplasty;
- allows a more lateral incision, directly over the rotator cuff tear, (avoid deltoid detachment);
- ref: Débridement of Partial-Thickness Tears of the Rotator Cuff without Acromioplasty. Long-Term Follow-up and Review of the Literature
- open rotator cuff repair
- arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
- References
Transtendon arthroscopic repair of partial-thickness, articular surface tears of the rotator cuff
Partial-thickness Articular Surface Rotator Cuff Tears: an All-inside Repair Technique
Pasta lesion-trans-tendon technique for repair