- See:
- Calcitriol
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Renal Failure: (Orders for the CRF Patient)
- Renal Spondyloarthropathy
- Vit D
- Effects on Adult Bone:
- abnormalities of renal function can produce profound bone disease;
- bone disease seen in renal failure is called renal osteodystrophy;
- early stages of osteodystrophy:
- effects on bone are primarily due to action of parathyroid hormone on osteocyte-osteoblast lining cell system, which is probably result of decreased phosphate excretion by the kidney;
- w/ decreased phosphate excretion, there is elevation of plasma phosphate & complexing of calcium & phosphate in bone fluid;
- as result, increasing amounts of PTH hormone are required to move the same amount of calcium from bone in order to maintain the plasma calcium at a constant level;
- due to elevated parathyroid hormone levels, there is increase in number of bone remodeling centers & increase in bone turnover; 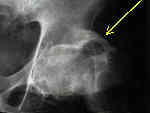
- late stages:
- when the glomerular filtration falls below 25% of normal, increased secretion of PTH is no longer able to maintain normal phospate levels, and the serum phosphate increases;
- mineralization of previously osteomalacic bone then occurs, and osteosclerosis develops; (see ossification of soft tissue);
- end stages:
- diminished ability of kidney to hydroxylate vit D leads to a decrease in circulating levels of 1,25(OH)2D3 & produces decrease in intestinal calcium absorption;
- calcification of osteoid is inhibited owing to deficiency of 1,25(OH)2D3, and owing to metabolic acidosis and other circulating inhibitors of mineralization that occur in uremic state;
- net effect of renal dz on bone:
- is combination of secondary hyperparathyroidism, osteomalacia, and osteosclerosis;
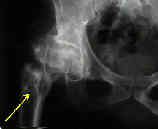
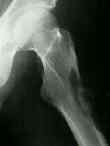
- when bone disease becomes severe, pathologic fractures may occur, esp in ribs, pelvis, and hips;
- uremic pts w/ advanced hyperparathyroidism appear prone to nontraumatic aseptic necrosis of the hips;
- bone pain, frx, and concomitant muscle disease may be the major impediment to rehabilitation in chronic uremia;
- Effects in Children:
- bone may appear diffusely sclerotic;
- varus deformity of the proximal femurs may occur as a result of bone softening and osteomalacia;
- growth plates are widened and zone of provisional calcification is poorly defined