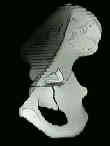
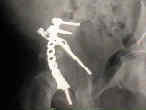
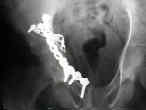
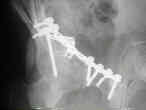
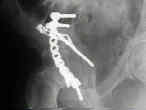
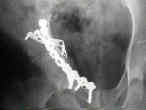
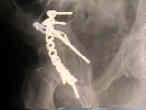
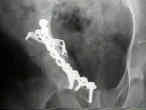
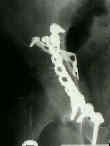
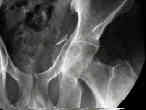
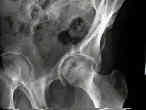
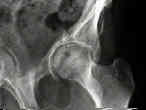
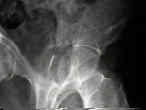
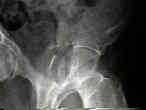
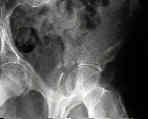
- See: Transverse Fractures of the Acetabulum
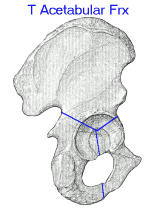
- Discussion:
- compared to other types of acetabular frx, the T Shaped - Posterior Wall Frx may
have the highest prevalence of poor clinical results;
- T shaped fractures which are known to be especially difficult, include those w/
a transtectal component, those w/ wide separation of the verticle fracture line,
and those w/ pubic rami fracture;
- Approach:
- frx is approached using Kocher Langenbock approach w/ pt prone;
- often a trochanteric slide osteotomy will be required for additional exposure;
- if a difficult reduction is expected, it is sometimes preferable to use the extended iliofemoral or triradiate incision;
- Reduction and Fixation of Anterior Column;
- distraction of posterior column frx line, allows visualization frx of anterior column on acetabular articular surface;
- anterior column is reduced w/ bone hook & pointed reduction clamps;
- anterior column is manipulated thru sciatic notch, or thru joint;
- fixation utilizes lag screws placed from posterior to anterior direction;
- if these maneuvers do not produce adequate reduction, subsequent ilioinguinal approach is required;
- Reduction of Posterior Column:
- posterior column is reduced and stabilize;
- frx may be approached & reduced as posterior column injury
The acetabular T-type fracture. A biomechanical evaluation of internal fixation.