- Deforming forces:
- Biceps brachii and Supinator inserts into the proximal1/3 of the radius;
- these muscles are the supinators of the forearm;
- Pronator Teres, originating above the elbow medially, inserts into the middle third of the radius;
- when frx is distal to insertion of pronator teres, proximal fragment lies in neutral rotation, and the distal fragment is pronated;
- Pronator Quadratus, located on the anterior aspect of the lower forearm, inserts into the distal third of the radius;
- when the fracture is distal to the insertion of the pronator teres muscle, the proximal fragment lies in neutral rotation, and the distal fragment is pronated;
- Brachioradialis
- assists in elbow flexion & is also semipronator & semisupinator of forearm of forearm, bringing it from supine or prone position to neutral rotation;
- extensors and abductors of the thumb act with Brachioradialis muscle in fractures of the distal third of the radius and pull the distal fragment of the radius proximally;
- Flexor muscles of the forearm:
- tend to pull the distal fragments anteriorly and produce dorsal bowing of the radius and ulna during healing;
- Proximal Third Frx :
- see pediatric proximal 1/3 forearm frx
- above insertion of pronator teres;
- proximal fragment of radius is supinated & flexed because of unopposed action of biceps brachii & supinator, and the distal fragment is pronated by the action of the pronator teres & pronator quadratus muscles;
- to obtain alignment of the fracture, the distal fragment should be supinated;
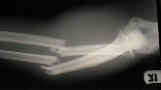
- Middle Third Fractures:
- below pronator teres teres;
- proximal fragment is held in neutral rotation, as action of supinator is countered by the pronator teres;
- proximal fragment is drawn into flexion by action of biceps;
- distal fragment is pronated & drawn toward ulna by pronator quadratus;
- to achieve anatomic reduction, distal fragment is brought into neutral rotation;
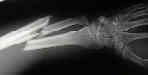
- Lower 1/3 of Forearm Fractures:
- distal fragment of the pulled radius is pronated & pulled inward by pronator quadratus;
- overriding & shortening are caused by obliquity of frx & pull of muscles
The effects of angular and rotational deformities of both bones of the forearm. An in vitro study.

