- Discussion:

- trapezius and serratius anterior stabilize scapular base from which the arm operates;
- trapezius, which arises from spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae & inserts on spine of scapula
and acromion, is innervated by spinal accessory nerve and branches from third and fourth cervical roots;
- its upper fibers shrug shoulder & aid in suspension of shoulder girdle;
- middle portion aids in adduction and rotation of the inferior angle of the scapula;
- lower segments, together w/ serratus anterior, clamp scapula to chest wall so that it cannot rotate or slip sideways;
- Innervation:
- inevated by branches of the ansa cervicalis and the spinal accessory nerve from 3rd & 4th cervical roots;
- note: that in the posterior cervical triangle, the spinal accessory nerve is located superficially in the subcutaneous tissue;
- Actions:
- its upper portion shrug shoulder & aid in suspension of shoulder girdle;
- middle portion aids in adduction & rotation of inf. angle of scapula;
- lower segments, together w/ serratius anterior clamp scapula to chest wal so that it cannot rotate or slip sideways;
- Upper Division:
- origin: external occipital protuberance, medial 1/3 of superior nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae & spinous process of 7th cervical vert;
- insertion: lateral 1/3 of clavicle and acromion process; 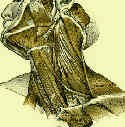
- action:
- rotation of scapula so glenoid cavity faces superior;
- when acting with the other sections of trapezius it adducts scapula;
- reversed origin insertion action:
- laterally flexes head and neck to side of contraction;
- rotates head and neck away from side of contraction;
- acting bilaterally, extension of the head and neck;
- nerve supply: spinal accessory and ventral ramus of C2, C3, C4;
- synergists:
- levator scapulae, clavicular head of sternocleidomastoid, middle and lower trapezius;
- Middle Division of Trapezius:
- origin: spinous process of 1st - 5 th thoracic vertebrae;
- insertion: superior border of spine of scapula, draws back acromion process;
- nerve supply: spinal accessory nerve and ventral ramus, C2, C3, C4;
- synergists: spinal accessory nerve and ventral ramus, C2, C3, C4;
- Lower Division Trapezius:
- origin: spinous process of 6th to 12th thoracic vertebrae;
- insertion: medial 1/3 of spine of the scapula;
- action:
- rotation of scapula to face the glenoid cavity superior gives inferior stabilization of scapula;
- aids to maintain spine in extension;
- draws back acromion process;
- nerve supply: spinal accessory nerve and ventral ramus, C2, C3, C4;
- synergists: trapezius upper and lower divisions;
- Paralysis of Trapezius:
- most often arises from mishandled cervical node biopsy, trauma, or from radical neck dissection (due to injury to spinal accessory nerve);
- clinical findings:
- drooping of the shoulder, lateral winding of the scapulae, and weak forward elevation of the shoulder and weakened shoulder abduction;
- patients may be more prone to brachial plexus palsy, frozen shoulder, subacromial impingement, and thoracic outlet syndrome;
- Modified Eden Lange Procedure:
- described by Eden in 1924 and Lange in 1959;
- attempts to restore the 3 anatomical and functional aspects of the trapezius;
- pt is placed in lateral position;
- trapezius is dissected off its origin of the scapular spine;
- levator scapulae and rhomboids are identified;
- each of these muscles are detatched from medial aspect of scapulae (along with a small piece of bone);
- levator scapulae is transfered laterally to scapular spine;
- replaces superior portion of trapezius;
- rhomboid minor is transferred to supraspinatus fossa;
- replaces middle portion of trapezius;
- rhomboid major is transferred to infraspinatus fossa;
- replaces inferior portion of trapezius
Transfer of the Levator Scapulae, Rhomboid Major, and Rhomboid Minor for Paralysis of the Trapezius.
Treatment of trapezius paralysis.
Surgical Management of Trapezius Palsy.

