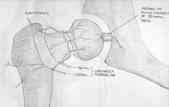
- blood supply for femoral head;
- external rotators of the hip
- Discussion:
- MFCA supplies majority of blood supply to femoral head;
- branches of MFCA enter capsule of hip joint near its distal insertion and couse proximally along femoral neck toward femoral head;
- medial femoral circumflex artery arises from posteromedial aspect of deep femoral artery and less commonly from the common femoral artery;
- its course is deep into femoral triangle, between pectineus and psoas & under neck of femur to the back of thigh;
- MFCA may send branches to adductor brevis & adductor magnus;
- forms an important astomosis: cruciate anastomosis ;
- five consistent branches of the medial femoral circumflex artery:
- deep branch: runs toward the intertrochanteric crest between pectineus medially and the iliopsoas tendon laterally along inferior border of obturator externus;
- main division of the deep branch crosses posterior to obturator externus and anterior to superior gemellus, obturator internus, and inferior gemellus;
- posterior to the tendon of obturator externus, and anterior to the tendons of superior gemellus, obturator internus, and inferior gemellus;
- runs in space between the quadratus femoris and the inferior gemellus
- perforates the capsule superfior to the insertion of superior gemellus and distal to piriformis;
- vessels course beneath synovial sheath of reflected portion of capsule of joint posterosuperiorly on the neck of the femur;
- trochanteric branch:
- branches off next to the proximal border of quadratus femoris, crossing over trochanteric crest toward the lateral aspect of greater trochanter;
- posterior branch: it can be identified in the space between the quadratus femoris and the inferior gemellus;
- anterior branch:
- anterior to quadratus femoris, MFCA artery divides into ascending branch to the trochanteric fossa of femur & transverse branch to
the hamstring muscles beyond the ischial tuberosity;
- preserving the attachment of the obturator externus tendon during surgery and dislocation protects the ascending branch of the MFCA from rupture and/or stretching;
- transverse branch appears between quadratus femoris & upper border of adductor magnus;
- runs adjacent to the proximal border of the quadratus femoris, crossing over the trochanteric crest toward the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter
Anatomy of the medial femoral circumflex artery and its surgical implications.
Vascularity of the Arthritic Femoral Head and Hip Resurfacing.
Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Deep Circumflex Iliac Artery
Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Femoral Artery
Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Profunda Femoris Artery
Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation: Medial and Lateral Femoral Circumflex Arteries