- Discussion:
- frx is associated w/ injury to arterial supply of minor fragement;
- this may be manifestated by AVN;
- vascular supply to proximal scaphoid:
- proximal two thirds to three fourths of scaphoid is supplied by vessels entering dorsal surface;
- vessels enter through dorsal ridge in 79%, distal to waist in 14%, & proximal to waist in 7%;
- vessels branched soon after entering bone and then coursed proximally and palmarly as far as the subchondral bone;
- natural history with non operative treatment:
- times to union increasing for more proximal frx;
- frx of distal third heal in approx 6-8 weeks;
- middle third frx heal in 8-12 weeks;
- frx of proximal third heal in 12-23 weeks;
- Treatment:
- consider operative treatment via dorsal approach;
- consider need for cancellous bone grafting;
- Complications:
- nonunion of proximal pole
- avascular necrosis of proximal pole
- Case Example:
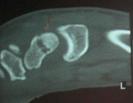
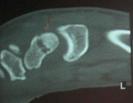
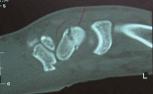
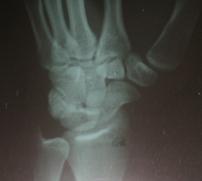
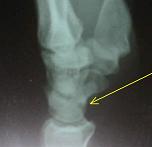
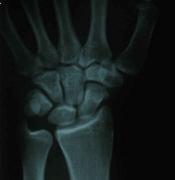
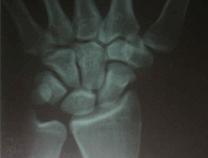
- 20-year-old male who sustained a fall on his outstretched hand;
- the fracture was missed on the initial films by the ER physician (careful review of the lateral view demonstrates the fracture);
- the second set of radiographs were taken three months later which demonstrated non union and early AVN;
Dorsal approach to scaphoid nonunion.
Management of Acute Fracture and Nonunions of the Proximal Pole of the Scaphoid.
Retrograde compression screw fixation of acute proximal pole scaphoid fractures.
Dorsal open repair of proximal pole scaphoid fractures
Retrograde compression screw fixation of acute proximal pole scaphoid fractures
Percutaneous fixation of the scaphoid through a dorsal approach: an anatomic study.