- Dicussion:
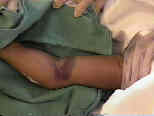
- assess for swelling and tenseness of the forearm compartments;
- assess carrying angles of the affected and non affected arms;
- r/o neurologic deficits
- median nerve injuries are more often associated w/ posteromedial displacement;
- AIN injuries are most common and occur w/ postero-lateral displacement;
- w/ posteromedial displacement, lateral spike of proximal fragment may tether the radial nerve;
- r/o vascular injuries:
- vascular injuries are more often associatted w/ posterolateral displacement;
- medial spike may tether brachial artery;
- it is essential to check and recheck not only the presence of a radial pulse but also its quality;
- remember that an intimal arterial injury can occur slowly over several hours;
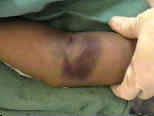
- skin changes:
- "dimple sign" occurs when a spike of bone penetrates brachialis muscle and anterior subQ tissues causing subQ hemorrage;
- if the brachialis is buttonholed by the distal humeral spike, then the muscle can be milked off the spike by grasping the proximal arm and squeezing sequentially from proximal to distal;
- avoid excessive medial squeezing (to avoid N/V injury);
- r/o compartment syndrome;
- note that median nerve injury can mask the symptoms of a compartment syndrome;
- olecranon & 2 epicondyles form a straight line in extended positition;
- when elbow is flexed to 90 deg, they form corners of triangle;
- shape of this triangle is unaltered in supracondylar frx of humerus but is distorted by posterolateral dislocation of elbow;
- associated injury:
- palpate distal radius for frx