- Discussion:
- superficial phlebitis
- proximal tibial anesthesia
- patellofemoral pain / pathology:
- references:
- Patellofemoral problems after intraarticular anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
- Patellofemoral problems after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
- Pain after use of the central third of the patellar tendon for cruciate ligament reconstruction. 33 patients followed 2-3 years.
- Infrapatellar contracture syndrome: diagnosis, treatment, and long term follow up.
- Deterioration of patellofemoral articular surfaces after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
- arthrofibrosis: / loss of motion;

- reference:
- The early treatment of motion complications after reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament.
- tibial tunnel syndrome: (see diagram to the right)
- tibial tunnel may enlarge following ACL reconstructive surgery;
- over a one year period the tibial tunnel may increase in diameter by 2 mm (average) over one year;
- ACL reconstruction failures:
- inadequate timing (early reconstuction is assoc w/ arthrofibrosis:);
- associated injuries (varus knee, significant osteochondral defects);
- improper placement of graft tunnels;
- impingement of the graft in the femoral notch;
- due to improper tunnel placement;
- due to inadequate notchplasty;
- inadequate graft fixation;
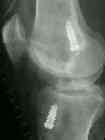
- Radiographic Evaluation:
- hyper-extension lateral view:
- allows assessment of percentage of impingement by intercondylar roof;
- a line is drawn thru the center of the tibial tunnel and a line is drawn tangential to the slope of the intercondylar
roof;
- note where these lines intersect in relation to to the tibial plateau;
- ideally, the anterior border of the tibial tunnel should be just posterior to the intersection of the intercondylar roof
with the tibial plateau
Reflex Inhibition of the Quadriceps Femoris Muscle After Injury or Reconstruction of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament.
Can muscle co-contraction protect knee ligaments after injury or repair

