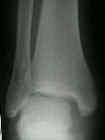
 - See: Radiographic Studies of the Foot and Ankle
- See: Radiographic Studies of the Foot and Ankle
- Mortise Views:
- syndesmotic injury;
- medial clear space should be less than 4 mm and superior- medial joint space w/ in 2 mm medially of its width laterally;
- due to the obliquity of the medial malleolus, measurement of medial clear space can be difficult on the Mortise view (in this case use AP view);
- talar tilt
- tibiofibular line
- talocrural angle
- AP
- medial clear space should be less than 4 mm and superior-medial joint space w/ in 2 mm medially of its width laterally;
- often, it is easier to measure medial clear space on AP view rather than mortise view due to obliquity of medial mortise;
- space between medial wall of fibula & incisural surface of tibia < 5 mm
- anterior tubercle of tibia should overlap fibula by atleast 10 mm;
- second method is to draw a line down the center of the tibia, & through center of the talar dome on both the AP and lateral x-ray;
- mortise width is usually 4 mm
Correlation of weightbearing radiographs and stability of stress positive ankle fractures.
Experimentally produced ankle fractures in autopsy specimens.
The key role of the lateral malleolus in displaced fractures of the ankle.
Examination of the pathologic anatomy of ankle fractures.
Ankle fractures. A clinical and roentgenographic stereophotogrammetric study.
Radiographic Measurement of the Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Has Limited Use

