- See:
- Calcar Femorale:
- Garden I & II:
- Garden III & IV:
- Garden's Alignment Index:
- Pathologic Hip Fractures:
- Radiology of the Hip:
- Sigh Index
- Radiographs:
- AP & Lateral of Ipsilateral Femur + Internal Rotation View;
- Lateral x-ray: of affected limb on the stretcher while good limb is flexed upto obtain the proper angle;
- lateral view: scrutinized for post. femoral neck comminution;
- do not order frog leg pts suspected of having a hip frx;
- Classification:
- Garden I & II:
- Garden III & IV:
- Garden's Alignment Index: 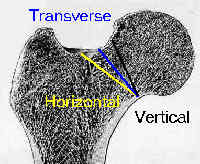
- Assessment of Risk of Non-union: (using modified Pauwel's method);
- see: femoral neck non-union:
- modified Pauwel's method classifies frx as horizontal, transverse, or vertical, according to direction of frx on femoral head;
- 11/11 Garden II frx w/ horizontal frx line had non-union;
- 2/5 Garden II frx w/ vertical frx line had non-union;
- 6/14 Garden III frx w/ vertical frx line had non-union;
- 2/5 Garden IV frx w/ vertical frx line had non union;
- references:
- Nonunion of Subcapital Femoral Neck Fractures.
- The Pauwels classification for intracapsular hip fractures: Is it reliable?
- Biomechanical analysis of a novel femoral neck locking plate for treatment of vertical shear Pauwel's type C femoral neck fractures.
- Non-displaced Frx: - if plain radiographs are negative, consider MRI for immediate interpretation or bone scan after three days;
- Radiographic Features:
- normal radiographic anatomy of the femoral head and neck reveal a convex outline of femoral head joining the concave outline of femoral neck
on all radiographic projections;
- this outline produces the image of an S or a reversed S curve;
- hence, the outline of the femoral neck is never tangent to the outline of the femoral head in a reduced femoral neck fracture;
- posterior comminution:
- frxs w/ posterior comminution have higher prevalence of non-union;
- degree of posterior comminution is most evident lateral radiograph;
- when treating fractures with a large amount of posterior comminution, surgeon should place the superior & posterior screws along calcar femorale to resist posterior collapse;
- Misc:
- single ramus fracture is commonly seen in elderly age groups, in whom falls are common;
- in this age group its important to make important distinction between frx of pelvis & undisplaced or impacted frx of neck of femur;
- finding tenderness over the pubic bone may make diagnosis apparent
Vertically oriented femoral neck fractures: mechanical analysis of four fixation techniques.
Vertical shear fractures of the femoral neck. A biomechanical study
Results of Internal Fixation of Pauwels Type-3 Vertical Femoral Neck Fractures

