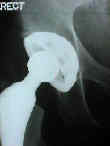
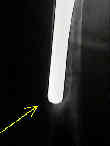
- Broaching:

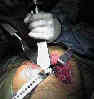

- broaching for cementless stems
- is usually started w/ the smaller broach or w/ broach 2 sizes smaller than templated during preop planning
- determination of anteversion
- exposure considerations:
- with smaller incisions, there will be a tendency of the broach to abraid against the skin;
- apply a surgical towel here to avoid skin trauma;
- Decreases in pulmonary artery oxygen saturation during total hip arthroplasty variations using 2 leg positioning techniques.
- remove soft medial cancellous bone:
- stems placed in valgus will have a thicker mantale of soft medial cancellous bone;
- failure to remove soft cancellous bone from medial surface of femoral neck will prevent the cement column from resting on a dense cancellous
support bed and may lead to early loosening;
- pulse lavage the canal:
- pulse lavage the canel to remove marrow and fat elements;
- references:
- Cemented versus noncemented total hip arthroplasty--embolism, hemodynamics, and intrapulmonary shunting.
- Massive cerebral fat embolism from hip surgery: a histologic study with alkaline phosphatase staining and thick celloidin sections
- Fat embolism and respiratory distress associated with cemented femoral arthroplasty.
- avoid over sizing the broach:
- if much resistance is met inserting the broach for the size chosen preoperatively, surgeon should then choose next smaller size femoral stem
rather than risk intraoperative femur frx;
- be especially aware of potential for fracture in osteoporotic patients as occured in this patient w/ cerebral palsy who was non wt bearing on operative side;
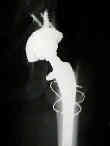
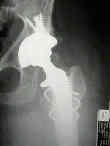
- the final broach is used a femoral trial; 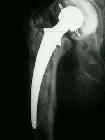
- avoid varus positiong:
- varus positioning is avoided by keeping the lateral edge of the broach up against the greater trochanter and by aiming the broach at the medial femoral condyle
Position, orientation and component interaction in dislocation of the total hip prosthesis.
The effect of anteversion on femoral component stability assessed by radiostereometric analysis.
Factors predisposing to dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. A multivariate analysis.
Femoral anteversion and restricted range of motion in total hip prostheses.
The effect of anteversion on femoral component stability assessed by radiostereometric analysis