- See:
- Proximal Humeral Physeal Injuries
- Condylar Fractures
- Discussion:
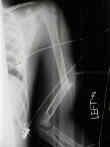
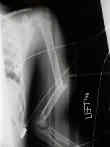
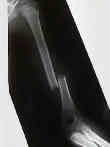
- while radial nerve paralysis occurs in adults, its rare in children;
- most represent neuorpraxias, & are expected to return w/ in 3-4 months;
- acceptable reduction:
- overriding of 1 to 1.5 cm is accepted, as overgrowth is common in pediatric fracture of the humerus;
- angulation should be less than 15-20 deg;
- Treatment:
- in infants and young children, immobilize frx for 4-6 weeks by immobilizing arm to side of chest in modified Velpeau bandage or sling & swathe;
- if fracture is unstable or too much overriding then apply lateral skin traction for 2 to 3 weeks until callus forms;
- in children, hanging cast method of treatment is not effective, since it requires compliance w/ pt in sleeping and staying in a semirecumbent or sitting posture w/o support beneath the elbow;
- Cast Position:
- long arm cast is applied from the MP heads to the axilla w/ elbow in 90 deg of flexion and neutral rotation;
- if frx is in distal third of humerus, place forearm in pronation;
- supinated position will result in a varus deformity at frx site;
- typically the cast/splint will have to be molded in valgus to counteract the varus angulation
- Flexible IM Nails: (synthes technique manual)
- Pediatric Humerus Fractures: Indications and Technique for Flexible Titanium Intramedullary Nailing
Biodegradable fixation of distal humeral physeal fractures.
Growth plate activity in the upper extremity.
Growth and predictions of growth in the upper extremity.
Fracture-separation of the distal humeral epiphysis.
Remodeling of Birth Fractures of the Humeral Diaphysis.
Fractures of the Distal Humeral Metaphyseal-Diaphyseal Junction in Children.