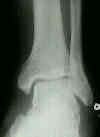
- Discussion:
- is taken in line with the long axis of the foot;
- entire fibula should be included if there is lateral joint tenderness above the joint line;
- this view is used to evaluate medial & lateral malleolus anterolateral tibia and proximal fibula;
- osteochondral frx of distal tibia and talus;
- articular congruity & measurements of relative mallellar length, syndesmotic integrity, and talar shift;
- TibioFibular overlap:
- on AP view indicates a proper syndesmotic relationship;
- space between medial wall of fibula & incisural surface of tibia should be less than 5 mm;
- anterior tubercle of tibia should overlap the fibula by at least 6 mm or 42% of fibular width;
- Stress Views:
- routine AP radiographic may show no lateral displacement of the talus, but an x-ray made when the ankle is stressed into supination and external rotation will show displacment and tilting of the talus in the mortise;
- External Rotation Stress Test:
- evaluates syndesmotic & deep deltoid ligament;
- on AP view differnece in width of superior clear space between medial and lateral side of the joint should be < 2 mm;
- these are static measurements of the talar position;
- in normal ankle, talus may tilt up to 5 deg w/ inversion stress;
- measurements of talar tilt using stress x-rays are used to evaluate lateral ligament stability;
- Technique:
- patient is supine with the heel resting on the cassette;
- foot is in neutral position, sole is perpendicular to leg & cassette;
- central beam is directed vertically to the ankle at the midpoint between the malleoli