- Discussion:
- proximal tibiofibular joint will prevent valgus correction unless fibula is shortened or tibiofibular ligaments are removed;
- transection if tibiofibular ligamets: (preferred technique)
- performed thru same incision as for osteotomy;
- proximal tibiofibular joint capsule is disrupted (may also remove inner 1/3 of fibular head), allowing the fibula to migrate
proximally;
- tibiofibular ligaments can be sectioned or portion of fibula to which they attach can be removed;
- if large correction is needed, however, fibular head, if retained, may impact on proximal tibial fragment as wedge is closed;
- in the study by Billings A, et al. (2000), not one of 64 knees that underwent high tibial osteotomy (using transection of the
tibio-fibular capsule) developed peroneal nerve palsy;
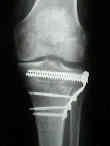
- fibular head transection:
- gives clear access to lateral tibial condyle, removes tibiofibular joint and ligaments, and allows for
reattachment of biceps tendon & fibular collateral ligament to neck of fibula under
physiological tension;
- w/ this technique, peroneal nerve can be visualized directly;
- the distal cut can be made directly thru the center of the fibular head;
- care is taken to protect the peroneal nerve;
- often the proximal fibular head fragment will fuse to the proximal tibia, as well as healing to the distal
fibular fragment;
- fibular transection:
- oblique transection in its prox 1/3 to allow overlap as osteotomy is closed;
- be aware of the danger zone of fibular osteotomy which lies between 70 mm and 150 mm from the
fibular head (which endangers nerve branches to the EHL)
The fate of fibular osteotomies performed during high tibial osteotomy
Danger Zones Associated with Fibular Osteotomy.
Palsy of the deep peroneal nerve after proximal tibial osteotomy. An anatomical study.

