- See:
- Anterolateral Bowing
- Neurofibromatosis
- Discussion:
- is rare, occurring equally in girls and boys;
- disease is almost always unilateral;
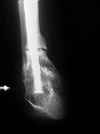
- acute frxs occur during first 2 yrs of life, usually shortly after birth.
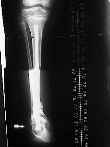
- associated w/ anterolateral bowing and neurofibromatosis;
- neurofibromatosis is present in approx 40-50% of pts w/ pseudarthrosis, while about 10% of pts w/ neurofibromatosis will have
pseudarthrosis of tibia;
- dysplastic type is characterized by narrowing, sclerosis, and obliteration of the medullary canal.
- cystic type shows no narrowing but instead has cyst-like areas which resembles fibrous dysplasia microscopically;
- in this type, leg appears normal early in course, w/ frx and pseudarthrosis occurring after 5 years of age;
- Non Operative Treatment:
- patellar tendon bearing - total contact orthosis, which is used to try to prevent frxs or to control developing ones;
- Surgical Treatment Options:
- once frx ensues, treatment includes open reduction, internal fixation, & bone grafting w/ autogenous graft with or w/o electrical stimulation;
- intramedullary rodding + bone grafting: (see osteogenic proteins)
- has mixed results;
- references:
- Extending intramedullary rods in congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia.
- Intramedullary fixation for congential pseuarthrosis of the tibia.
- Treatment of Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia with Recombinant Human BMP-7 (rhBMP-7). A Report of 5 Cases.
- limb lengthening:
- vascularized fibular transfer:
- may still leave the involved leg w/ potential for frx, angulation, & growth disturbance;
- references:
- Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia. Long-term followup of 29 cases treated by microvascular bone transfer.
- Vascularized fibular grafts in the treatment of congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia.
- syme's amputation:
- indicated for congential pseudoarthrosis with limb length inequality greater than 5 cm and or severe foot deformity;
- presence of pseudoarthrosis by itself is not an indication for amputation;
- note that amputation thru pseudoarthrosis may leave scars over amputation stumps, and over growth phenomena may end up requiring
additional revision amputations;
- in some cases, spontaneous union of pseudarthrosis will occur (due to total contact of prosthesis and beneficial effects of wt bearing;
- references:
- The Syme amputation in patients with congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia.
- Spontaneous union of a congenital pseudoarthrosis of the tibia after syme amputation.
- Amputation for congential pseudarthrosis of the tibia. Indications and techniques.
Congenital pseudarthrosis of the leg. Late results.
Late-onset pseudarthrosis of the dysplastic tibia.
Surgical treatment of congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia.
Pathology and natural history of congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia.
Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia. A long-term follow-up study.
Residual challenges after healing of congenital pseudarthrosis in the tibia.